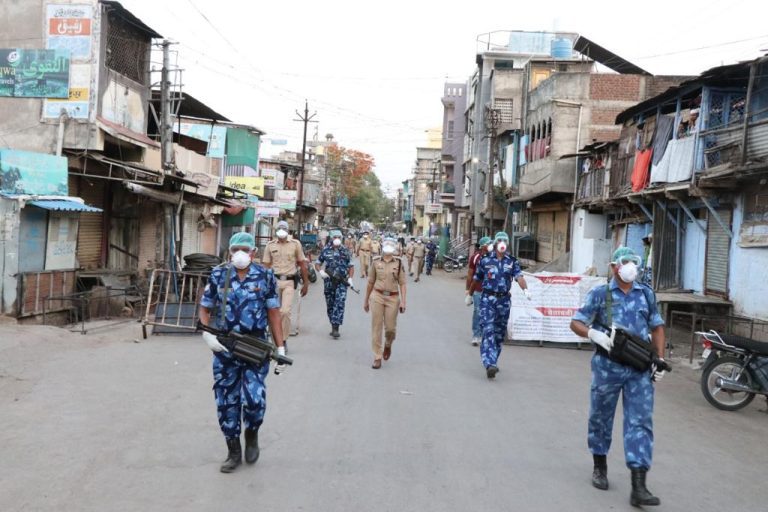
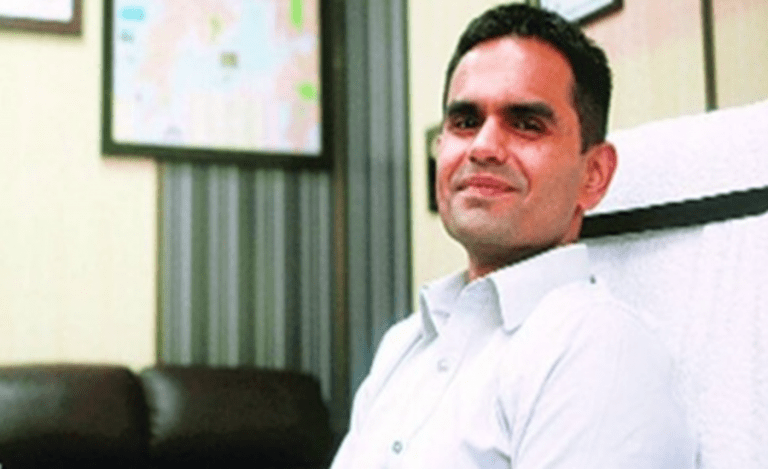
Of all the major cities of India, Mumbai was the first to have put the coronavirus to mat. The first metropolitan city, it’s also known as the financial capital of the country, which brought the dreaded positivity rate of Covid 19- the measure of the spread of the disease in a population- to a single digit (of 9.9 percent). At the forefront of Mumbai’s corona warriors is the Additional Commissioner of Brihanmumbai Municipal Corporation (BMC), Mr Suresh Kakani. Our correspondent Pallavi Priya spoke in detail with him to find how he and his team achieved this enviable target.
Q: Sir, how exactly did you go about in combating Covid 19 in Mumbai?
Mr Kakani: Mumbai is a geographically very constrained city, and the density of population here is tremendously high. So it was really challenging for us to control the virus. For this we applied multi-pronged strategy because the basic concept was tracking, testing and treating. Suppose the patient is coming positive to, then the task was to identify his close contacts or the high-risk contacts. That was rule no.1. And rule no 2 consisted of taking the high risk contacts from his place of residence to the quarantine center, keeping that person in the quarantine center for 14 days. During this period, we also took care of all his basic all basic necessities which included medicines and regular checkups.
Q: Did the BMC also set up quarantine centers to keep such high risk people in isolation:
Mr Kakani: Yes, of course. We have created the quarantine centers to start with. All of are well equipped with necessary facilities. These may not be of star categories but all the basic amenities were there so people were also happy to be there. Normally people do not want to go to quarantine centers, but in Mumbai they happily got themselves admitted here. Then subsequently we also developed the jumbo facilities when we realized that the existing infrastructure was not sufficient enough to accommodate more number of people. The people in quarantine centers should be away from the normal patients, otherwise cross infection will become an issue, and will affect doctors, nurses and paramedic staffs as well. With all these things in mind, we developed jumbo facilities having 2000 and even 3000 beds, equipped with oxygen supply and ICU facilities. These centers came to our rescue in a big way.
Q: How did you go about roping in doctors in your anti-Covid 19 drive?
Mr Kakani: We went about this through standardized protocol, in consultation with the task force (set up for this purpose). We took on board doctors from everywhere: whether they were specialists working in private sector or in public sector in Mumbai. They would regularly give advice about the treatment protocol and how to handle different kinds of patients. At the same time, we used to monitor such patients through CCTV as well, so as to know if he is being treated properly or he requires the services of a specialist doctor.
Q: In a quarantine centers, no family member, friend or relative is allowed to meet the patients. How did you ensure that he or she did not suffer pangs of loneliness and depression?
Mr Kakani: We realized that could be an issue. Many times, we provided the patients with a tab and smartphones, so that they could connect with their family members through video calls. This played a major role in helping them with their trauma. We believe that because of these measures, the overall panic level among the patients went down considerably. Because of this, the people’s confidence in the BMC too has shot up.
Q: What other steps did you take as part of your overall strategy to control Covid 19 in Mumbai?
Mr Kakani: One big decision we took concerned decentralization of the bed allocation. This was important, because Mumbai is geographically divided into 24 wards. Initially we had only one center and control room from where we used to manage everything. But this led to overburden at that centre. At times, even telephone calls could not be handled properly- there would be so many of them. Thereafter we decentralized it and set up 24 different ward rooms. Thus it became easier to manage the patients and take care of their individual needs. At each ward room, medical teams and ambulances were stationed, and they ensured that the patients got proper care, medication and treatment at all hours of day or night.