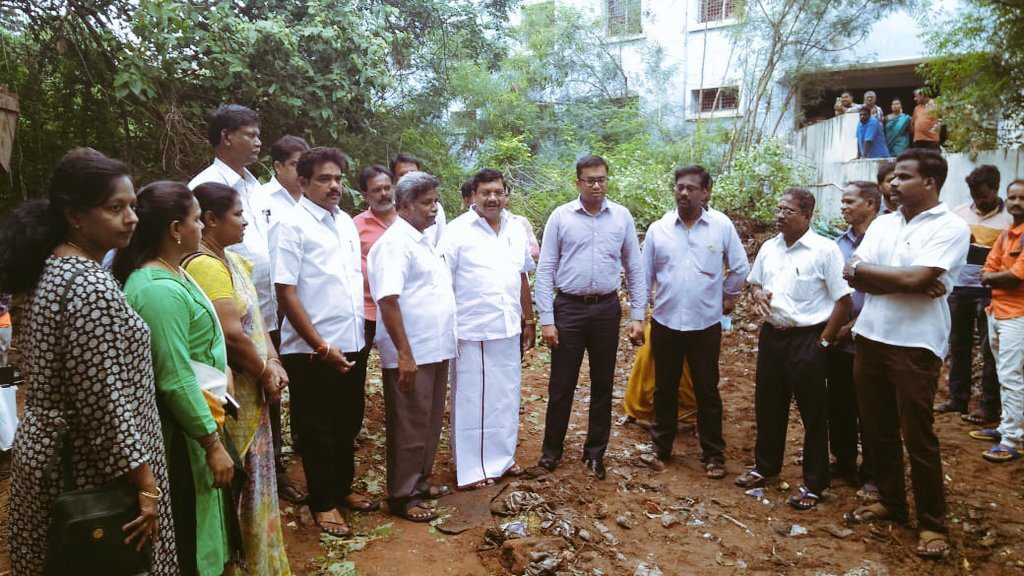
By carrying out perhaps the first digital mapping of water bodies in a big swathe of land anywhere in the country, District Collector of Puducherry in Tamil Nadu, Dr T Arun has done something really remarkable. His efforts, which involved community participation of the people of Puducherry, have resulted in restoration of 198 water bodies such as lakes, ponds and wells.
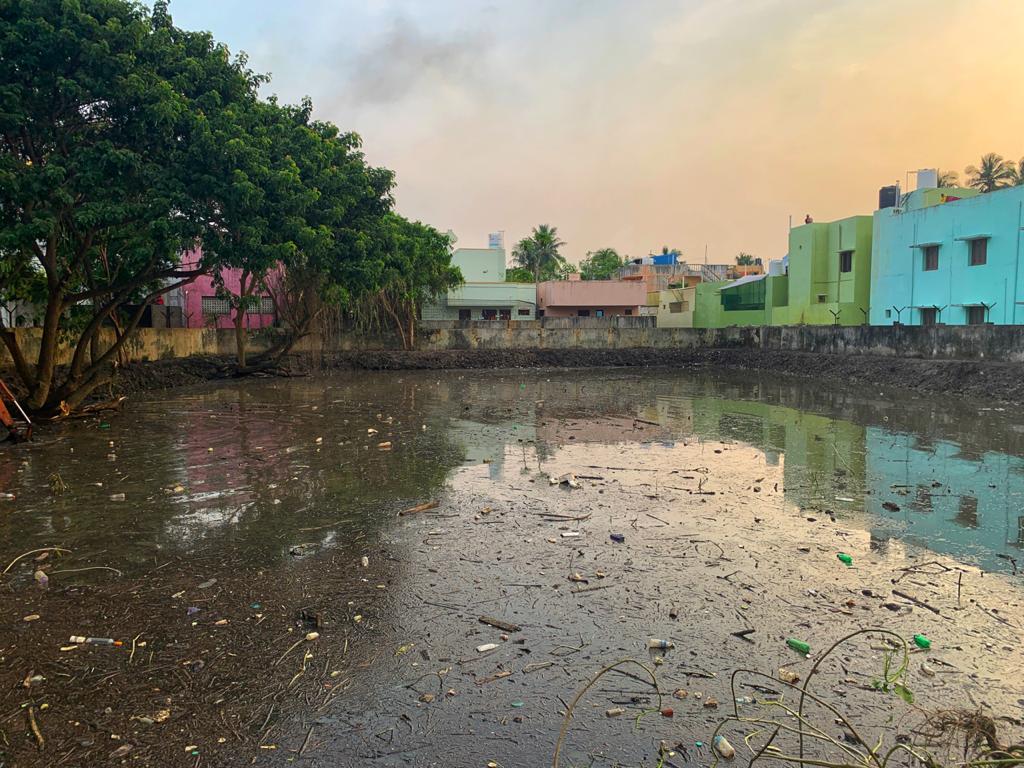
Let’s understand the importance of Dr. Arun’s achievement. The farmers of Puducherry had been suffering for a long because their crops would get water either during monsoon or the retreating monsoon. The water sources in the district had either dried up or had been conveniently “hidden from the view’’ by land encroachers in various parts of the city.
Puducherry’s Distressed Farmers
Until Dr. Arun arrived at the scene, the agriculture community of Puducherry had nobody to look upto. All their efforts to get water for their crops hit the wall. This was when Dr. Arun, a 2013-batch IAS officer decided to do something. He went through the issue methodically, in a systematic manner.
Speaking with Indian Masterminds, Dr. Arun said the first step was perhaps the most important. “This,’’ he explained, “was the identification of water bodies which the land encroachers had hidden from us. Initially, when we managed to distill 10-20 water bodies, the response from people was tremendous. Thereafter, we had no trouble in community mobilization. The support of the people came to us from all sides, enabling us to launch the `Neerun-Oorum’ project (which essentially means water and the villages). This gave a sense of entitlement to the people and they participated whole-heartedly in the project.’’

The next important step was to get the land records authenticated- and look for the hidden water bodies. For this, said Dr. Arun, “meetings with Municipalities/Community `panchayats’ were held to sensitize all the Blocks with regard to the project. Revenue officials who are the custodian of the land helped in the surveys and identification of water bodies.’’
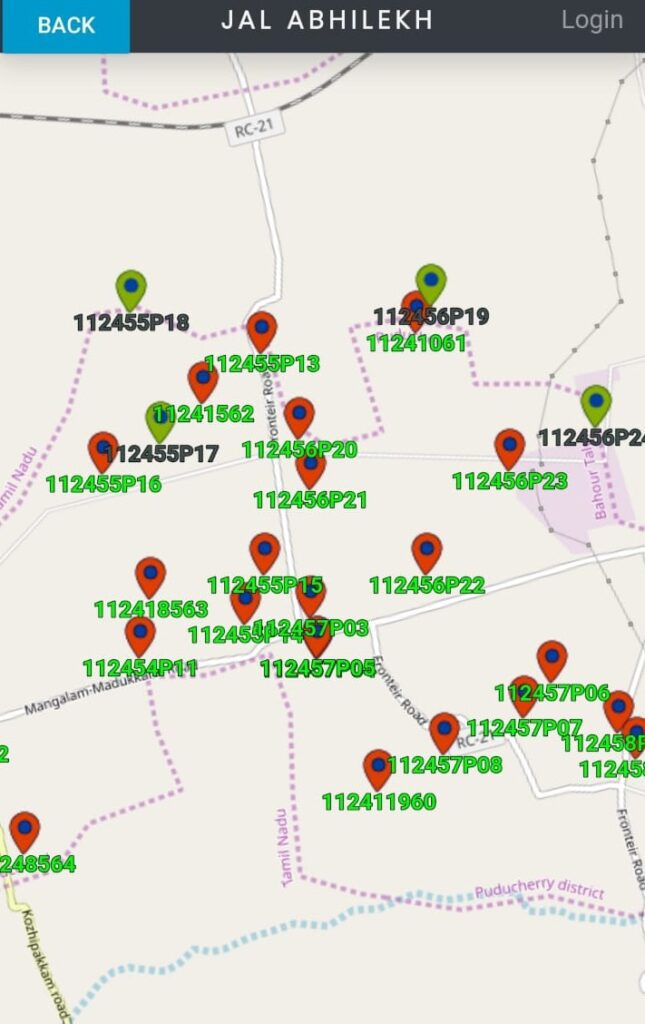
After identifying the water bodies, the district administration of Puducherry gave a unique ID number to each one of these, thus removing any possible confusion by way of duplication of names of various lakes and ponds. “The mass awareness programmes launched by mobilized over 60,000 people. A large number of women and schools too were roped in. Ultimately, it led to farmers and other stakeholders taking the responsibility of inclusive water governance,’’ said Dr. Arun.

COMMUNITY MOBILISATION AND DIGITIZATION OF WATER BODIES
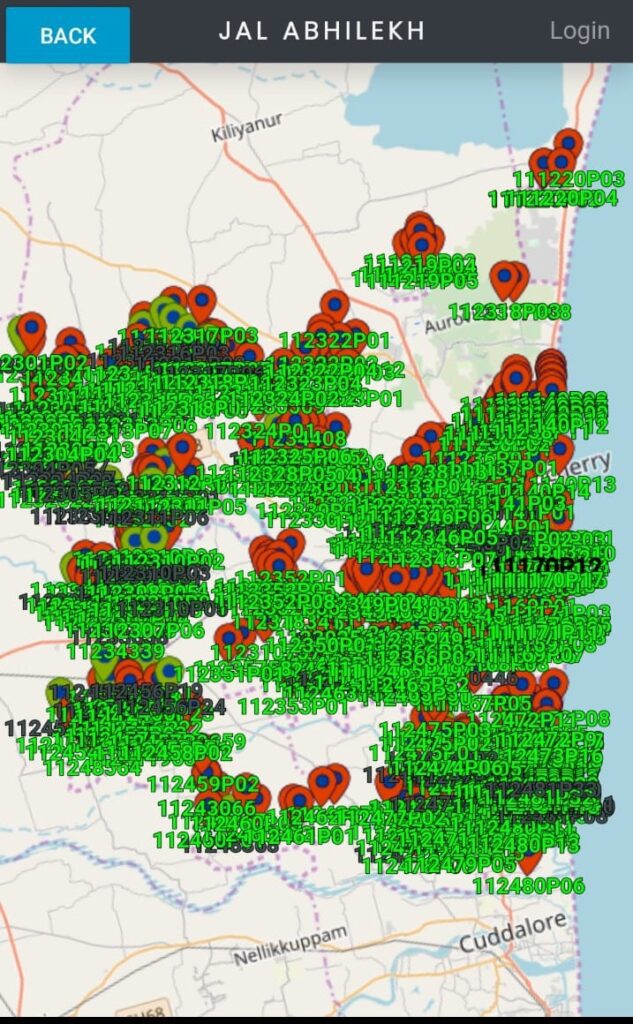
Soon thereafter, the district administration launched the `Jal Abhilekh/Neer Padhivu’ App in Puducherry, in collaboration with CSIR-National Environmental Engineering Research Institute, Nagpur. This is the first application in the country which enabled digitization of all water bodies in a district. The app essentially o identifies the water bodies with Unique ID & geo-tagging, location, extent, type of encroachment. It also updates the status of water bodies online. Apart from this, the app contains day-to-day notifications of circulars and orders regarding the water bodies. With the help of a remote sensing satellite, the app also gives information about important parameters like the rise in groundwater level and increase in the humid moisture content of the soil.
THE OUTCOME
With the involvement of the community, 198 water bodies have been rejuvenated and a stretch measuring 206 kms of canals desilted). About 78,000 saplings were also planted around each and every water body, with the help of 32 NGOs. Pointed out Dr. Arun, “our drive also helped in raising the groundwater level. As per the Central Ground Water Authority, 15 feet of groundwater has been increased in some areas. ‘’

Due to the intensive efforts put in by the Dr Arun’s community, 24 water bodies listed in the community `panchayats’ earlier increased to impressive. But Dr Arun’t work is far from over. The big plan is to restore all the 684 water bodies in Puducherry. But certainly, the start has been spectacular.