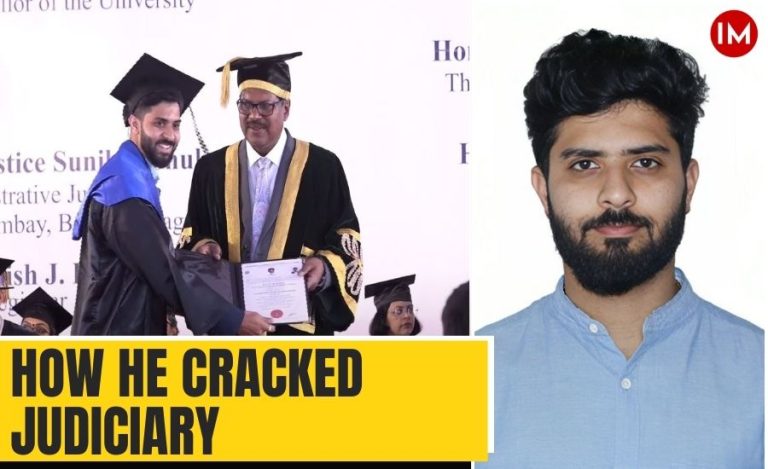
Prayagraj, a city revered for its spiritual and historical significance, is hosting the Maha Kumbh Mela 2025, which began on January 13. Known as the confluence of the sacred rivers Ganga, Yamuna, and the mythical Saraswati, Prayagraj attracts millions of pilgrims and tourists for this grand religious gathering. The event is not only a spiritual spectacle but also a monumental logistical challenge. To meet the environmental demands posed by the influx of visitors, the Prayagraj Municipal Corporation has undertaken an ambitious project of urban greening, employing the Japanese Miyawaki technique to establish dense forests across the city.
Over the past two years, under the leadership of Municipal Commissioner Chandra Mohan Garg, IAS [2016 batch, Uttar Pradesh Cadre], the Corporation has transformed over 55,800 square meters of urban land into lush green oxygen banks. This initiative has created a healthier atmosphere for residents and visitors alike, addressing pollution and enhancing biodiversity. With over 10 locations converted into thriving green spaces, these forests are a demonstration of the city’s commitment to sustainability and environmental restoration.
MIYAWAKI FORESTS: AN URBAN GREENING REVOLUTION
The Miyawaki technique, developed by Japanese botanist Akira Miyawaki, focuses on planting native species densely to mimic natural forests. This approach accelerates tree growth, allowing plants to mature up to 10 times faster than traditional methods. In Prayagraj, this method has turned barren and polluted areas into green havens, providing a practical solution to urban pollution and ecological degradation.
The largest plantation site, located in the Naini industrial area, features 1.2 lakh trees comprising 63 different native species. Another notable transformation occurred in Baswar, a former garbage dumping yard, where 27,000 trees of 27 species have been planted. These efforts have revitalised degraded lands, reduced dust pollution, and improved air quality. Additionally, these green spaces have addressed long-standing issues such as bad odours and industrial waste management.
ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT AND BENEFITS
Miyawaki forests offer a plethora of environmental benefits. By improving soil quality and enhancing biodiversity, these forests contribute to ecological balance. They prevent soil erosion, reduce air and water pollution, and create habitats for various species of birds, insects, and small mammals. Moreover, dense forests help regulate temperatures, lowering the ambient temperature by 4 to 7 degrees Celsius, which is particularly beneficial during the city’s scorching summers.
The diverse range of species planted under this project includes mango, neem, peepal, tamarind, mahua, bamboo, and teak. Medicinal plants like tulsi, brahmi, and arjuna, along with ornamental varieties such as hibiscus, bougainvillaea, and gulmohar, enhance the aesthetic ecological value of these forests. Fruit-bearing trees like amla and lemon provide food for local fauna, blending environmental conservation with cultural heritage.
A SUSTAINABLE VISION FOR MAHAKUMBH AND BEYOND
The establishment of these forests reflects the foresight and dedication of the Prayagraj Municipal Corporation under Chandra Mohan Garg, IAS. These efforts are not limited to preparing for the Mahakumbh but also aim to create a lasting legacy of environmental stewardship. By prioritising urban greening and sustainable development, Prayagraj is setting an example for other cities to follow.
As the Mahakumbh unfolds, the Miyawaki forests stand as a green testament to the city’s proactive approach to tackling environmental challenges. These green spaces are not only enhancing the experience for millions of devotees but also ensuring a healthier and more sustainable future for the residents of Prayagraj.