Today is World Rhino Day, and the Union Minister for Environment, Forest and Climate Change, Mr. Bhupender Yadav, started the day with a message that conveys the Indian government’s commitment to conserving this megafaunal species: “India has a long history of conserving one-horn rhinoceros. It’s a matter of pride that poaching of rhinos in Kaziranga has gone down to the lowest in the last two decades. Kudos to all involve in the effort.”
Indeed, it’s a matter of pride that sustained conservation efforts and zero tolerance to poaching have brought down poaching in Kaziranga to an all-time low, from 30-35 cases a year till a few years back to only 1 case last year. Simultaneously, Manas Tiger Reserve in lower Assam has scripted a success story of its own in reintroducing rhinos in its area, from zero few years back to 51 rhinos now.
On this special day dedicated to rhinos, we take a look at the success stories of rhino conservation and reintroduction in Assam, and also throw a quick glance at the special messages from forest officers who are closely tied to wildlife conservation in the country.
RHINO CONSERVATION IN KAZIRANGA
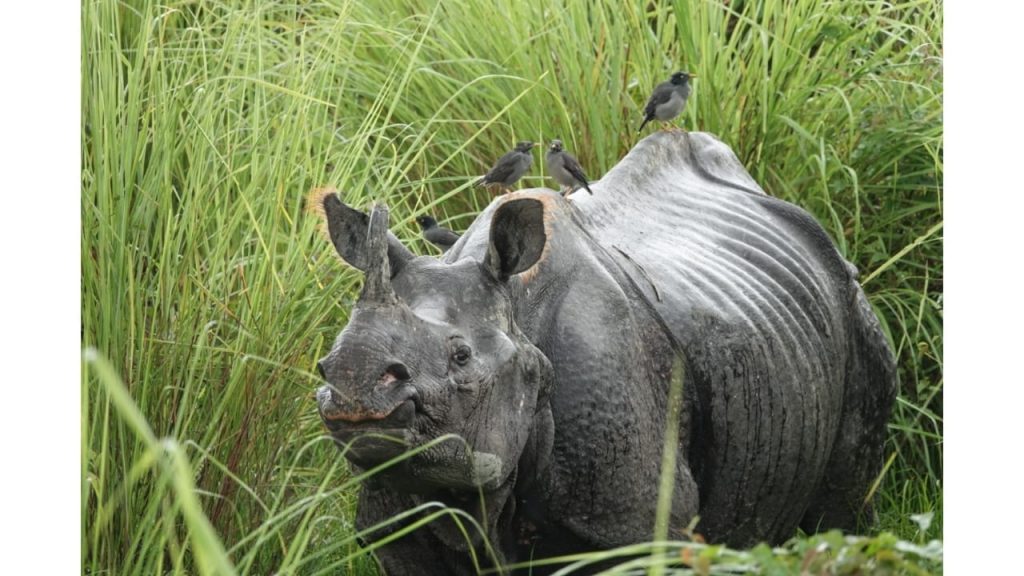
The conservation efforts for the Greater One Horned Rhino in Kaziranga started in 1902 and was necessitated by severe decline of the rhino population, mainly due to rampant poaching. That the sustained efforts have brought success can be borne out by the fact that in Kaziranga Tiger Rserve (KTR) now, the rhino population has increased more than 100 fold. At last count, it stands at 2613.

Field Director of Kaziranga, Mr. Jatindra Sarma, IFS, told Indian Masterminds: “From the beginning, our focus has been on anti-poaching activities. Joint patrolling mechanism with police, involving fringe villagers, strengthening civil administration have been successful in curbing rhino poaching. Now emphasis is being laid on making available more space, recovering habitat in new areas, habitat management in existing areas, wet land management, grassland management, and monsoon management. During the monsoons, flooding of riverine areas is an annual phenomenon, so managing animals crossing the NH to higher ground outside the KTR is a challenging task.”
The day was observed by Kaziranga management with multiple activities like bicycle rally, street drama, extempore speech, and lot more.
REINTRODUCTION OF RHINOS IN MANAS
Rhinos had disappeared from Manas Tiger Reserve in Assam as a result of civil unrest in the region in 1980s and early 1990s that had led to widespread poaching, deforestation and fragmentation. After the situation in the region stabilized, the Assam Forest Department took up restoration of the greater one-horned rhino in Manas as a priority.
The return of the one-horned rhinos to Manas is a powerful example of how sustained efforts and consistent focus can restore wildlife. The rhino population rebuilding was done through a combination of community engagement, animal rehabilitation and habitat conservation.

Re-establishing rhinos was challenging because they are very territorial, and adults moved from one habitat to another often fail to thrive. So, a new approach was also explored. Orphaned rhino calves from Kaziranga National Park were rehabilitated and then released into Manas when they were 2 or 3 years old, an age at which they are more able to establish their own territory. Orphaned rhino calves are rehabilitated in the Centre for Wildlife Rehabilitation and Conservation (CWRC) near KTR and raised until they can be moved to a soft-release facility in Manas before being set free into the wild.
Field Director of Manas, Mr. Vaibhav Mathur, IFS, told Indian Masterminds: “Day-to-day monitoring of released rhinos was subsequently taken up after the capacity of forest frontline was built up. As an ongoing process, the department is seeing to it that the habitat for rhinos does not deteriorate over time and habitat management interventions are being taken up annually. This has taken the rhino number to 51 till now.”
He also said that, to tackle poaching and human-animal conflict, community-based conservation activities and alternate livelihoods were introduced. Local communities were imparted training to boost anti-poaching efforts and equip rangers. And the children were educated through dedicated campaigns to take pride in their natural heritage.
FIVE RHINO SPECIES FOREVER
This is the theme of this year’s World Rhino Day. There are a total of five species of rhino – white, black, greater one-horned, Sumatran and Javan. The goal of this day is to promote awareness about the need to save rhinos from danger to their lives. Rhino day is celebrated both offline and online. Governments and organisations unite on this day to work towards the goal of taking care of all the five species of rhinos in Asia and Africa.
Calling the Indian rhino vulnerable, IFS officer Parveen Kaswan tweeted:
It is #WorldRhinoDay. There are 5 species of Rhino in the world. Among them the Black, #Sumatran and #Javan rhinos (which was once found naturally in India also) are critically endangered. And Indian rhino is Vulnerable. Here standing in its habitat with all the glory. pic.twitter.com/513ovaGCPu
— Parveen Kaswan, IFS (@ParveenKaswan) September 22, 2022
Drawing attention to Dudhwa’s success story of reintroduction of one horn rhinos, senior IFS officer Ramesh Pandey tweeted:
Today is World Rhino Day. We have proudly conserved this mega herbivore species in Terai-Duar and Brahmaputra floodplains.
— Ramesh Pandey (@rameshpandeyifs) September 22, 2022
Dudhwa is a success story where they were one horn rhinos were reintroduced in 1984 and now there population is around 40.
PC: Shared #WorldRhinoDay pic.twitter.com/rvWrffJWx4
While lauding the zero tolerance policy of Assam government towards poaching, IFS officer Sivakumar Periyasamy, currently posted as CCF, Southern Assam Circle, told Indian Masterminds that for sustainable conservation of rhinos, however, “we have to move from protected area specific approach to landscape approach by connecting habitats through corridors.”