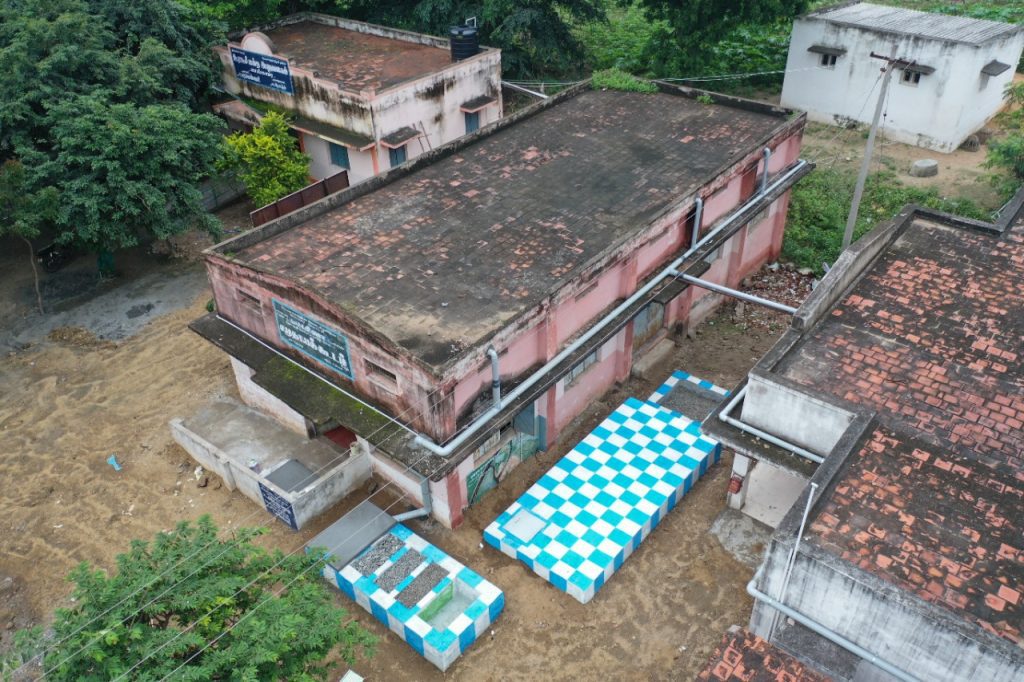
The district administration of Dindigul in Tamil Nadu has set an example for other districts by taking rainwater harvesting to another level. The district has already entered various record books for its rainwater harvesting initiatives. It has earned a place in Elite World Record Agency, Asian Records Academy, India Records Academy and Tamilian Book of Records by setting up 611 rainwater harvesting (RWH) structures in the shortest span of 21 days.
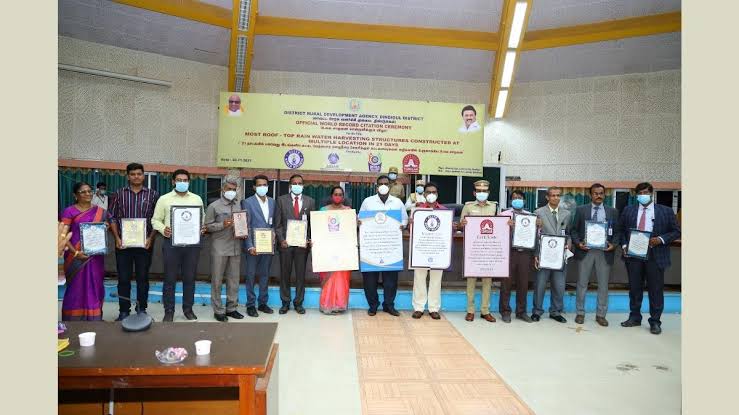

Indian Masterminds interacted with District Collector of Dindigul, S. Visakan, to get details about their rooftop rainwater harvesting initiative that has attracted worldwide attraction.
AIM
The main objective is to conserve every drop of rainwater and put it to immediate use. Conventional rooftop rainwater harvesting structures aim at collecting the rooftop rainwater and letting it into a soak pit for groundwater recharge. However, “In this rooftop rainwater harvesting method, the rainwater collected in the rooftop is filtered and stored in the sump and reused for various purposes like hand washing, toilets, utensil cleaning, etc,” explained DC S. Visakan.

METHOD
While sharing details about the method of RWH, the officer further said that the rainwater collected on rooftop was filtered using a filter media and stored in the sump.
In case of more than one building, junction chambers were built to ensure necessary gradation. The rainwater thus channelized is then let into a filtration media. “The filtration media contains three layers of metals in descending sizes. The filtration media could either be a vertical or horizontal soak pit depending on the need and area availability. This ensures that the water is cleansed of silt and impurities,” he said.

There are four chambers in the filtration media of which the first and last chambers contain a silt trap. The other three chambers contain metal and sand in descending order of sizes. Wire mesh is provided before each chamber’s outlet to ensure that the metal does not get washed away into the sump. The water, after passing through all layers of the filter media, is then let into the sump.
“The sumps are built from sizes varying from 9000 litres to 27000 litres depending on the rooftop area. The sump is provided with an outlet which will lead to a nearby abandoned bore well/open well or soak pit which is converted into a recharge structure,” Mr. Visakan explained.

Thus, during normal rains, the collected rainwater would be filtered and stored in the sump. During heavy rains, the excess water would flow from the sump through the outlet pipe into a nearby abandoned bore well/open well or soak pit which is converted into a recharge structure. The water is pumped to an overhead storage tank using this motor.
BUILDINGS USED FOR RWH
Mr. Visakan said that in the initial phase, 611 government buildings, like Panchayat Union Schools, Panchayat Office Buildings, E-service centres, were chosen to establish these rainwater harvesting structures. “As these structures have been built across majority of Panchayat Union primary and middle schools, it has now been ensured that these schools will be water self-sufficient,” he said.

Adequate care has been taken by the administration to sensitise teachers about the usage of the water for purposes like toilets, hand washing and utensil washing. “Teachers have been strictly instructed to not use this water for drinking water purpose,” the officer said.
HUGE STORING CAPACITY
The total sump capacity built across 611 locations in 21 days was 80 lakh litres. Thus, in a single rain, Dindigul district is now equipped to store 80 lakh litres of water for reuse. “A rainfall of 1mm over an area of one square meter will provide us with 1 litre of water. The combined area of buildings taken up for building rainwater harvesting structures in Dindigul is 1,03,033 square meters,” Mr. Visakan informed.

Dindigul district receives an average rainfall of 1000 mm per year. Thus, the capacity to store and reuse rainwater in Dindigul district in a year is 10.3 crore litres of water which is equivalent to the storage capacity of a small dam.