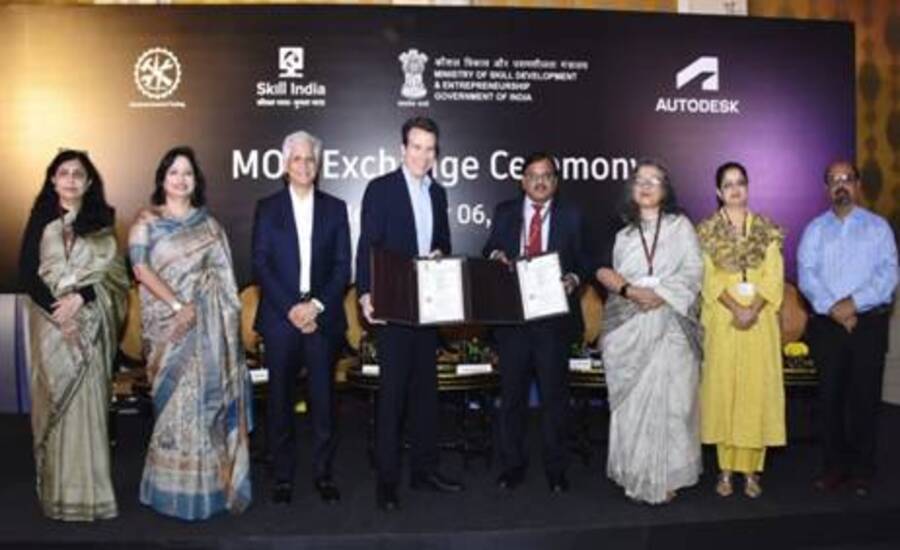
New Delhi: The Directorate General of Training (DGT), under the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE) and Autodesk Inc. have formalised a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) aimed at enhancing digital design and make skills across the country.
This collaboration is poised to modernise the training landscape in India’s vocational institutes and equip young learners with future-ready competencies.
Background of the Autodesk DGT MoU
Vocational education in India has been undergoing a transformation. The DGT manages thousands of Industrial Training Institutes (ITIs) and National Skill Training Institutes (NSTIs) that train lakhs of youth annually.
Read Also: Teaching Advanced Digital Skills: How to Go Beyond Basic Computer Use in the Modern World
According to the release, DGT oversees over 14,500 ITIs and 33 NSTIs. Meanwhile, Autodesk is a global leader in digital design, engineering and manufacturing software.
With industries evolving at a rapid pace—driven by design automation, 3D printing and AI—vocational training needs to keep up. The MoU recognises this need: it links DGT’s scale and vocational network with Autodesk’s technology and design expertise.
Key Details of the Autodesk DGT MoU
- The agreement covers over 14,500 ITIs and 33 NSTIs across India.
- It will enable educators, trainers and students to access professional-grade design & make software from Autodesk.
- The partnership focuses on industries such as architecture, engineering, manufacturing and construction—areas where digital design and “make” skills are in high demand.
- Importantly, it emphasises the emerging importance of AI-related abilities: as per Autodesk’s “State of Design and Make Report 2025”, 52 % of Indian organisations surveyed expect AI skills to be their top hiring priority.
- The initiative involves joint development of curricula, learning programmes and hands-on training modules—bridging the gap between academic learning and real-world industrial practices.
Importance of Autodesk DGT MoU
1. Scale and reach: Reaching thousands of ITIs and NSTIs means this initiative has the potential to impact hundreds of thousands of students and trainers.
2. Industry-alignment: As India aims to become a manufacturing and design hub, equipping students with software tools and design skills is critical.
3. Future-ready skills: The inclusion of AI, manufacturing technology, design automation shows the push for skills beyond traditional vocational trades.
4. Educator & trainer empowerment: The focus is not only on students but also on up-skilling faculty and trainers—key to sustained change.
5. Global technology alliances: For India to compete globally, collaborations like this help bring world-class technology and curricula into local training.
What to Expect Next
- Implementation of customised curricula and learning modules in ITIs/NSTIs using Autodesk’s software ecosystem.
- Certification programmes that validate students’ and trainers’ competencies in design & make technologies.
- Hands-on training sessions, faculty development workshops and industry-integrated projects.
- Monitoring of how AI-skills and digital manufacturing capabilities improve employability of vocational graduates.
- Potential expansion of software access, newer technologies (3D printing, additive manufacturing, IoT in design) over time.