In the heart of Tadoba Andhari Tiger Reserve (TATR), where the teak forests stand tall and the bamboo groves whisper wild secrets, one tiger has become the subject of both awe and concern. Known to wildlife lovers as “Chhota Matka”, T-126 is no ordinary big cat. His life has been a saga of dominance, survival, and conflict.
For years, Chhota Matka roamed fearlessly, his lineage linking him to the famed Matkasur, another legendary tiger of Tadoba. Conservationist and filmmaker Atul Joshi has often spoken of him with admiration, calling him “a shadow of his father – powerful, fearless, yet increasingly vulnerable to the pressures of living close to humans.” His name, often discussed in documentaries and by wildlife tourists, is etched into Tadoba’s living folklore.
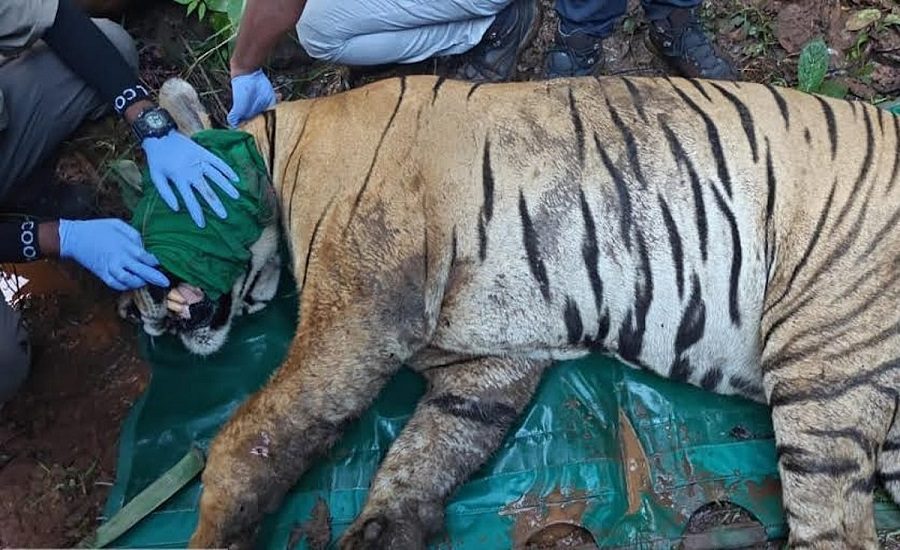
But recently, this magnificent tiger’s story has taken a dramatic turn. He had been injured so badly in territorial fights with other tigers that he had to walk on three legs only. His front left leg was so injured that he couldn’t even put it on the ground. It was a pathetic sight for his admirers. That was when the most dramatic turn came in his life. T-126 was captured by forest officials – a move that stirred curiosity, debate, and even emotion among those who had followed his journey.
Speaking exclusively to Indian Masterminds, Tadoba’s Field Director and 2011 batch IFS Prabhu Nath Shukla explained the decision: “The tiger has been captured as part of a management decision aimed at ensuring the safety of both local communities and the animal itself. We wish to clarify that this action is not an interference in natural processes such as territorial fights, which are normal in the wild. The capture was undertaken primarily to prevent potential human – wildlife conflict.”
FEEDING ON CATTLE
In recent weeks, Chhota Matka’s movements had changed. Once a forest king feeding on natural prey, he had started preying largely on cattle. His repeated visits to villages, close to human settlements, raised alarm. The danger was two-fold – villagers losing livestock, and the tiger facing retaliation from frightened communities.
Shukla pointed out the pressing reality: “In recent weeks, the tiger had been preying mainly on cattle and making repeated visits to villages, which posed a serious risk to both villagers and the tiger. Human presence and fear-driven reactions could have endangered the animal as well. This step was therefore necessary to minimize human interference, safeguard the community, and ensure the well-being of the tiger.”
PREVENTING THE CONFLICT
For Tadoba’s management, this was not a question of interfering in the natural order. Tigers fight, compete, and sometimes fall in territorial battles – that is nature. But this was different. Chhota Matka’s proximity to humans meant his life was at risk not from rivals, but from conflict that could spiral out of control.
Wildlife enthusiasts, however, see this as yet another reminder of the fragile balance between humans and big cats in tiger reserves. Filmmaker Atul Joshi, who has documented Chhota Matka’s life, remarked earlier this year that “T-126’s increasing ventures into village zones are signs of shrinking safe spaces. His story shows us that conservation is not just about protecting tigers – it’s about managing coexistence.”
WHAT HAPPENS NEXT?
Forest officials say Chhota Matka will undergo medical evaluation, and after treatment and assessment, he may be released back into a safer part of the reserve. His story is still being written, but one thing remains clear: T-126 is not just another tiger – he is a symbol of Tadoba’s ongoing struggle to balance the wild and the human.
As the sun sets over Tadoba, painting the forest in shades of amber, the question lingers: Will Chhota Matka once again walk free, reclaiming his throne in the jungle – or has this chapter marked the beginning of a more contained future?
Either way, his legacy, whispered in hushed tones by villagers and narrated with reverence by conservationists, will remain etched in Tadoba’s living memory.