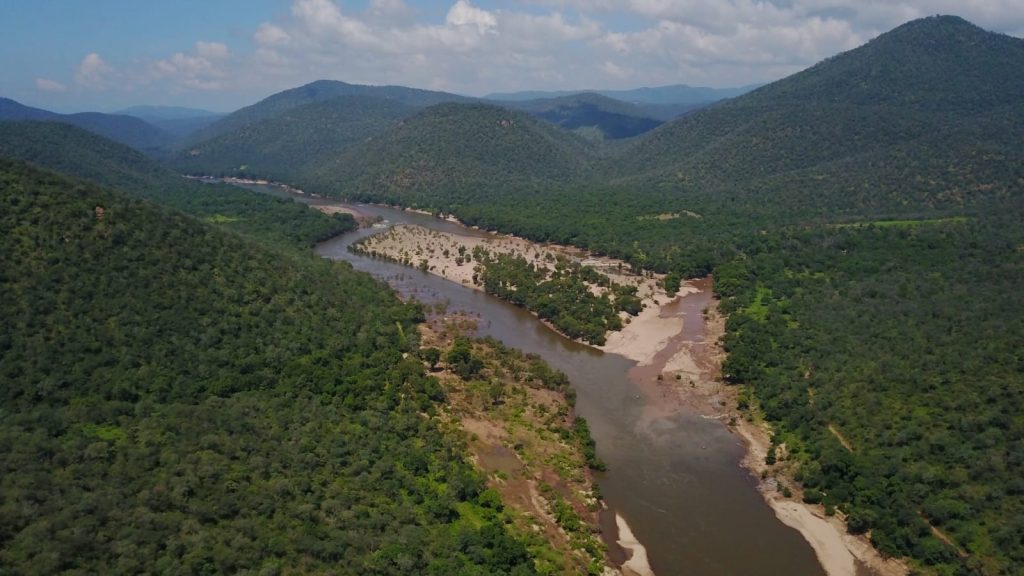
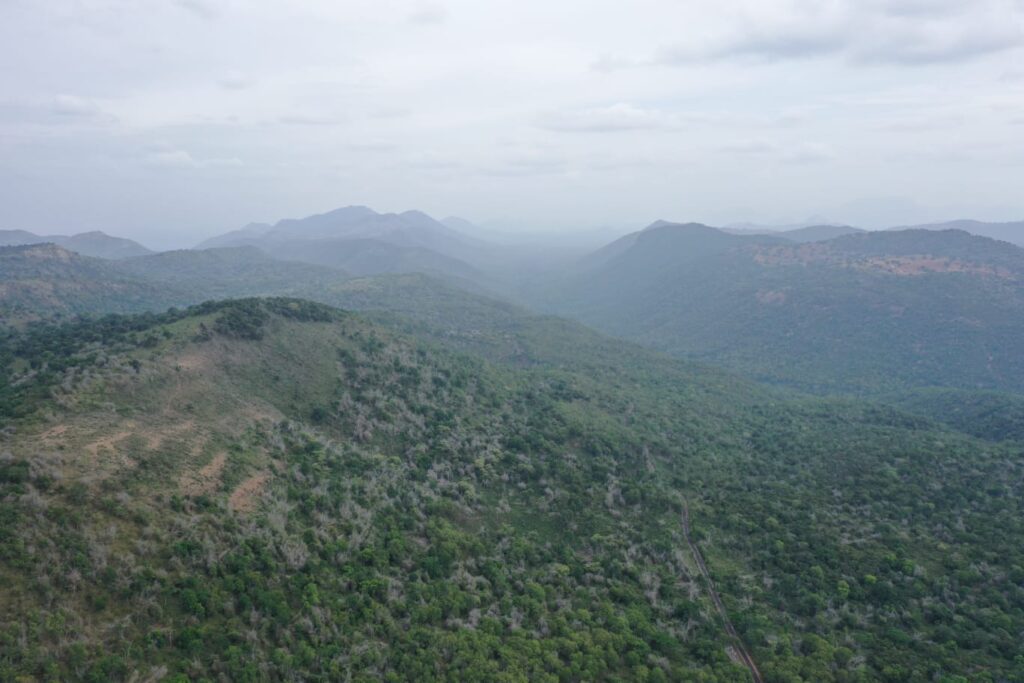
The Cauvery South Wildlife Sanctuary has become the 17th Wildlife Sanctuary of Tamil Nadu, after the state government notfied it. The sanctuary covers reserve forest areas in Krishnagiri and Dharmapuri districts, and is home to 35 species of mammals, 238 species of birds, Leith’s soft-shelled turtles, smooth coated otters, marsh crocodile and four horned antelopes.
Speaking with Indian Masterminds, IFS officer Karthikeyani, DFO, Hosur Division, shared why the Cauvery South sanctuary is a paradise for wildlife.
CAUVERY SOUTH WILDLIFE SANCTUARY
The sanctuary comprises of the 15 Reserve Forest areas in Anchetty, Urigam and Jawalagiri Ranges in Anchetty Taluk of Krishnagiri District and 5 Reserve Forest areas in Pennagaram and Palacode Ranges in Pennagaram and Palacode Taluks of Dharmapuri District, to an area of 686.406 sq.km.

“It is located between the Cauvery North Wildlife Sanctuary of Tamil Nadu and Cauvery Wildlife Sanctuary in the State of Karnataka. The area has adequate ecological, faunal, and floral significance and needs management as wildlife sanctuary for protecting and conserving wildlife, habitat, and to mitigate human-elephant conflict,” Ms. Karthikeyani said.
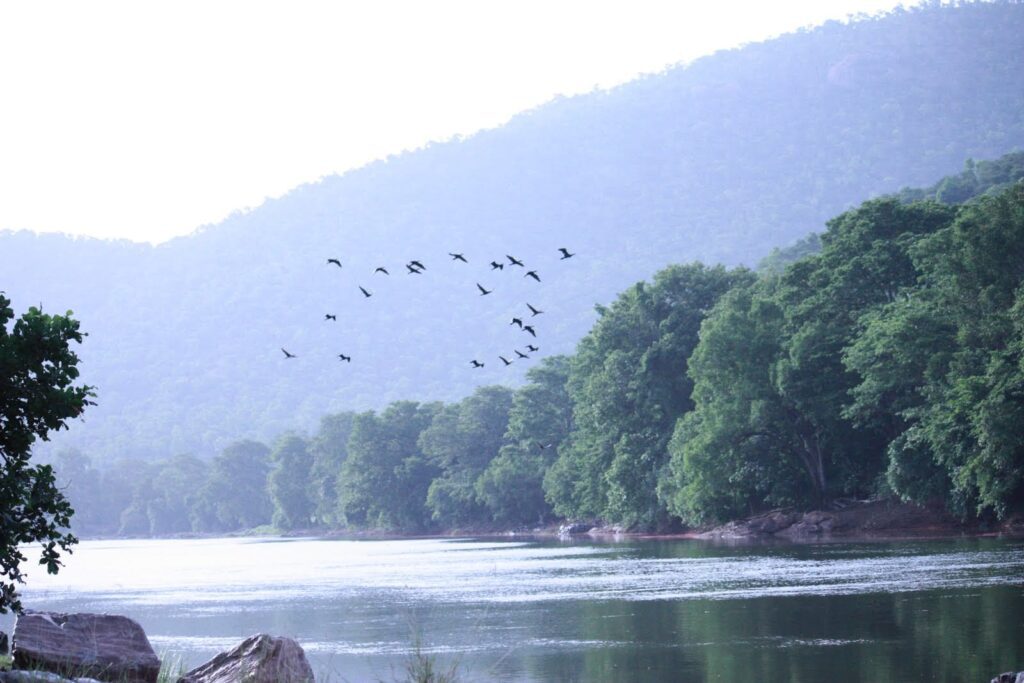
She further informed Indian Masterminds that the sanctuary area is a large, contiguous network of protected areas, enabling uniform legal status and protection along both the banks of the river Cauvery for a stretch of over 50 km. This landscape maintains further continuity to the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve through Male Mahadeshwara Wildlife Sanctuary, Billigiri Rangaswamy Forest Division of Tamil Nadu.
ELEPHANT HABITAT
“The sanctuary is an important elephant habitat in Southern India and is critical for a large number of riverine species dependent on river Cauvery. This area forms a unique ecosystem of the Cauvery basin and constitutes the last forested low-lying stretches of the Cauvery River before it enters the Stanley Reservoir,” Ms. Karthikeyani informed.
The area is large and has two important elephant corridors, namely, the Nandimangalam-Ulibanda Corridor and the Kovaipallam–Anebiddahalla Corridor.

RICH IN BIODIVERSITY
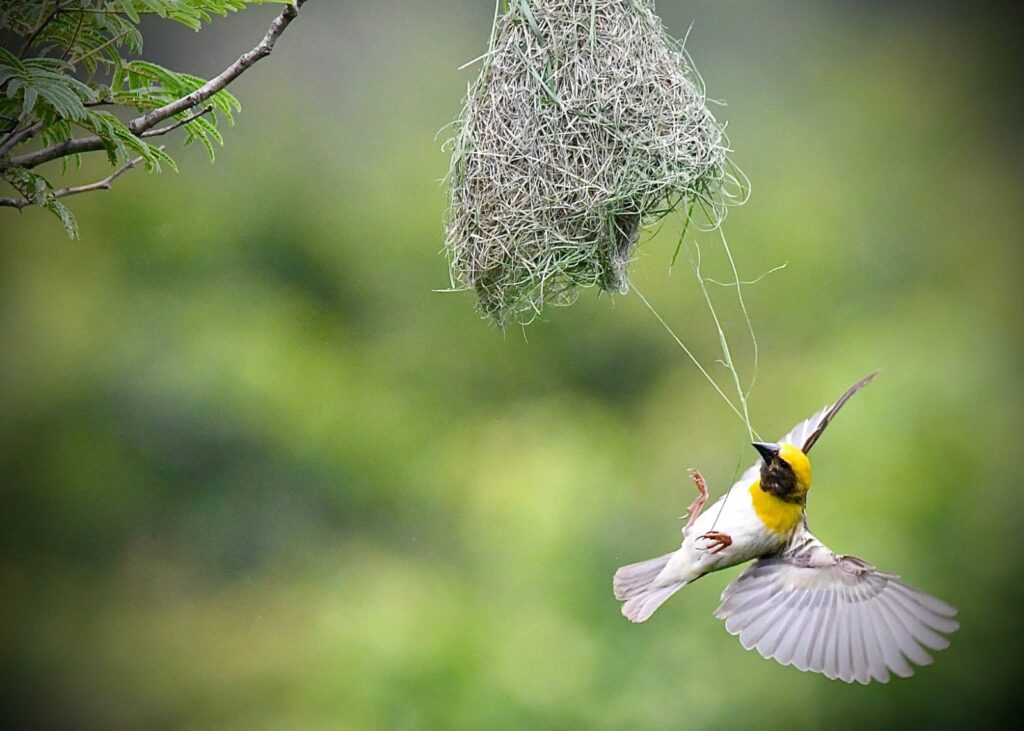
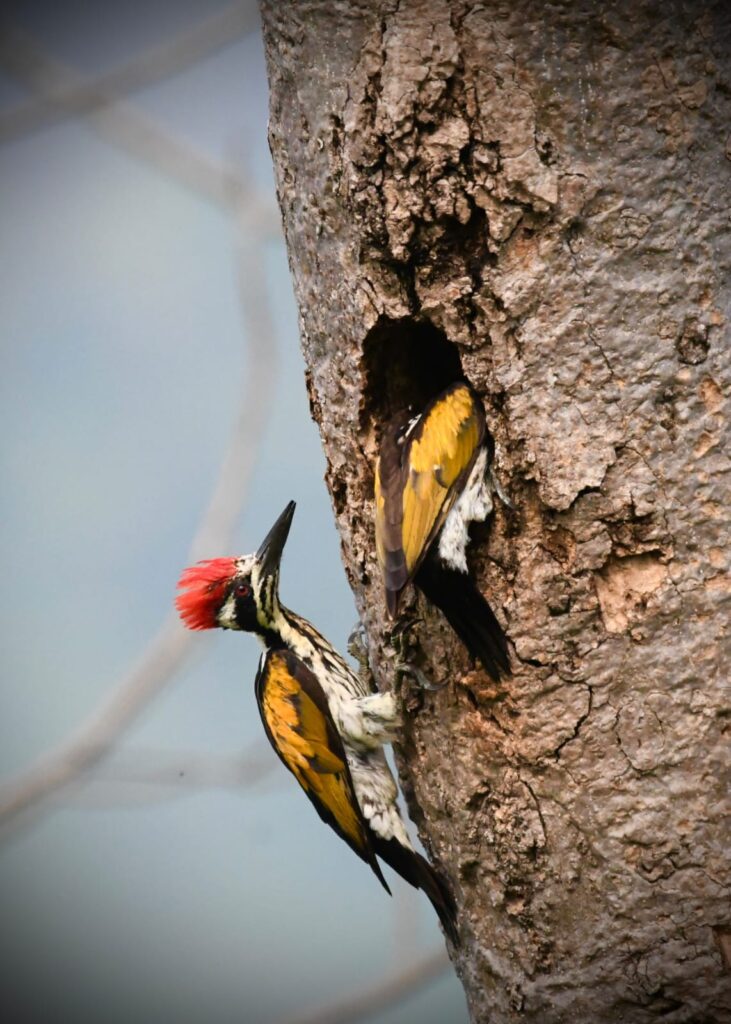
It is also rich in biodiversity, with at least 35 species of mammals and 238 species of birds. Some of the animals such as Leith’s Soft-shelled turtles, Grizzled Giant Squirrel, Smooth-coated Otter, Marsh Crocodile, Four-horned Antelope, Lesser Fish Eagle etc., are almost exclusively dependent on the Cauvery River and its riverine forest ecosystem. They are also red-listed and are in urgent need of focused conservation efforts and protection of their habitat.

“The sanctuary is also a successful tiger conservation progect, as the adjacent contiguous areas such as Male Mahadeshwara Wildlife Sanctuary and Banerghatta National Park in Karnataka have created a spill over effect and tigers have now begun to occupy these traditional ranges where they had been locally extinct for a few decades,” Ms. Karthikeyani said.
The forest areas of this sanctuary are part of the same landscape, and enhanced protection and habitat improvement have led to recovery of prey base and the area can now support tigers once again, as it had in the past. It also supports the conservation of leopard and other red-listed large carnivores.

GOVERNMENT SANCTION
Further, for the preparation of the detailed project proposal for improving the sanctuary, the Government of Tamil Nadu has sanctioned Rs. 5 crores.
“The creation of the sanctuary will make available grants from the state and centrally sponsored schemes for all kinds of recurring and non-recurring expenses, including creation of waterholes for providing water facilities to wild animals, establishment of anti-poaching camps, capacity building, arms and ammunitions, creation of barriers and maintenance in the sanctuary area. All this can be used to protect the forests and wildlife for a better and long-term conservation process,” Ms. Karthikeyani said.

She further shared that although people have an apprehension that because of the sanctuary notification, they will now get evicted outside, this is a miscommunication and a fake apprehension.
“The sanctuary has been notified only for enhancing the protection of the wildlife inside the forest and to increase the fund flow of habitat management. It will help the people in the end,” Ms. Karthikeyani concluded.