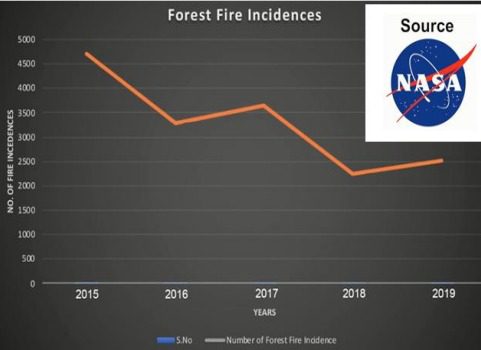
IFS officer Dr Abdul Qayum’s mobile app, E-Forest Fire, has helped in reducing forest fires in Arunachal Pradesh by 31%, in comparison to the last five year’s data (2015–20).
Dr Qayum, who is currently posted as Deputy Conservator of Forests in Chandigarh, took the help of technology and data, and did a lot of ground study to finally come up with the mobile app to predict forest fires. The initiative was acknowledged by the central government as the officer along with his whole team were presented with a national award for the same.

FOREST FIRE ISSUES IN HILLY AREAS
While speaking with Indian Masterminds, Dr Qayum said, “In 2018, when I was posted in Tawang district, a big fire broke out in the forests. The major issue of forest fires in hilly areas is that, it is out of human control as it happens in very high altitudes. This is when we thought of ideating a method through which forest fires can be predicted beforehand and forest department and government officials can act accordingly.”
For that, the forest department studied various strategic factors which were causing forest fires in the region. The geospatial technology towards forest fire characterization and evaluation of relationship with meteorological thematic layers was the main aim of the study, which was published by Springer, a German multinational publishing company of books, e-books, peer-reviewed journals in science, humanities, technical and medical (STM) publishing.
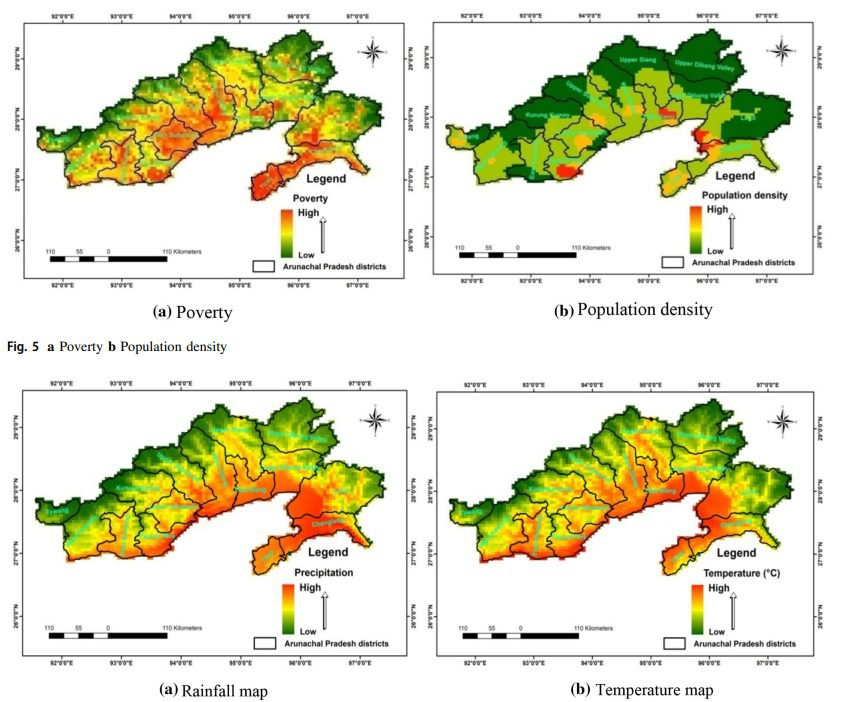
Factors like poverty, population density, temperature, rainfall, humidity etc., were identified and their impactswere also assessed.
FACTORS PERTAINING TO FOREST FIRE
Dr Qayum further said, “In the second stage, we studied the data which was available with the Forest Survey of India (FSI). The premier institution publishes data of the reports of forest fires in various parts of the country.”
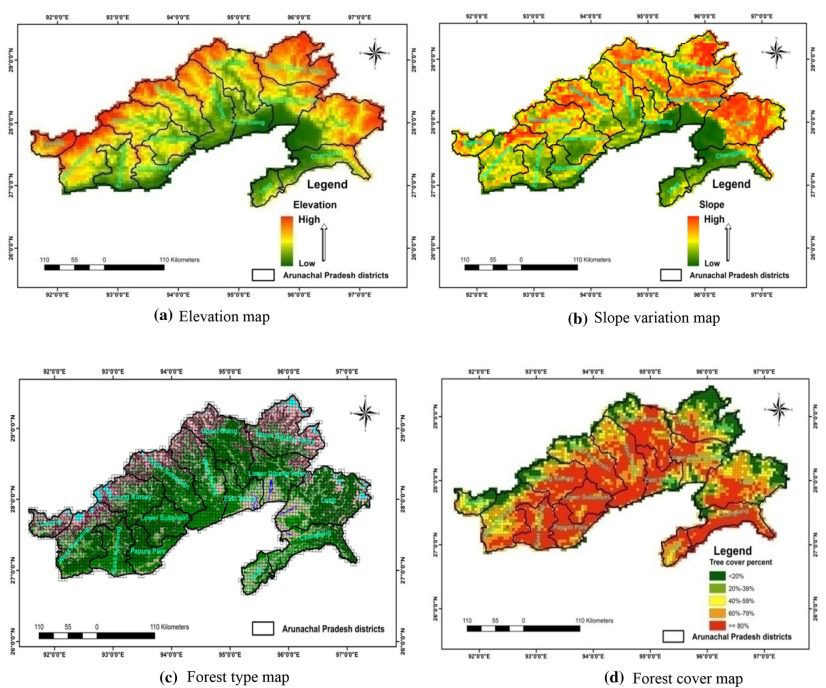
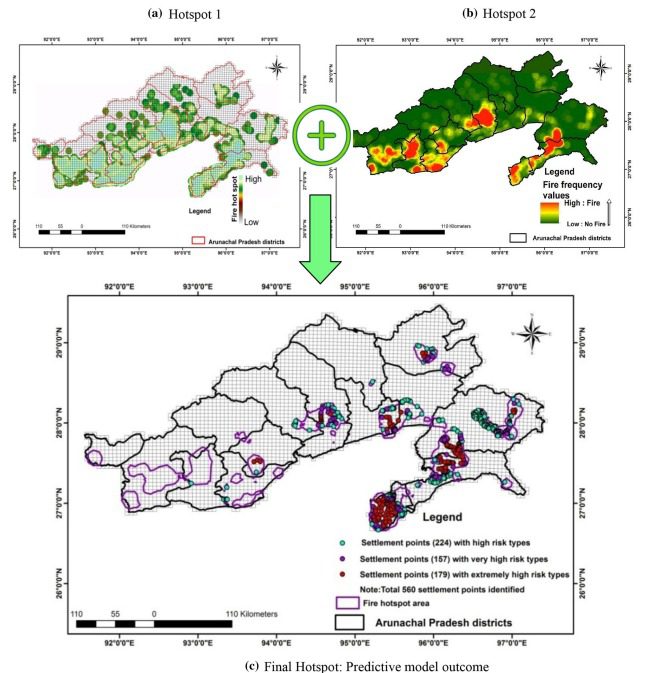
Spatial analysis of forest fires in Arunachal was carried out based upon the decadal (2008–2016) forest fire count datasets, which was assessed for spatial variability over the known Himalayan biodiversity hotspot in diverse geographical and socio-economic gradients.
Result suggested that Kameng districts had maximum fire incidences (25.2%) whereas it has 15.2% of state forest, establishing the districts as ‘forest fire hotspots’ in the state. Maximum number of incidences (88%) occurred in areas of low elevation (< 1500 m). There was high correlation with socio-economy where 42.3% forest fire points falls in high poverty index areas and 73% of fire incidences in the areas having population density 6–50.
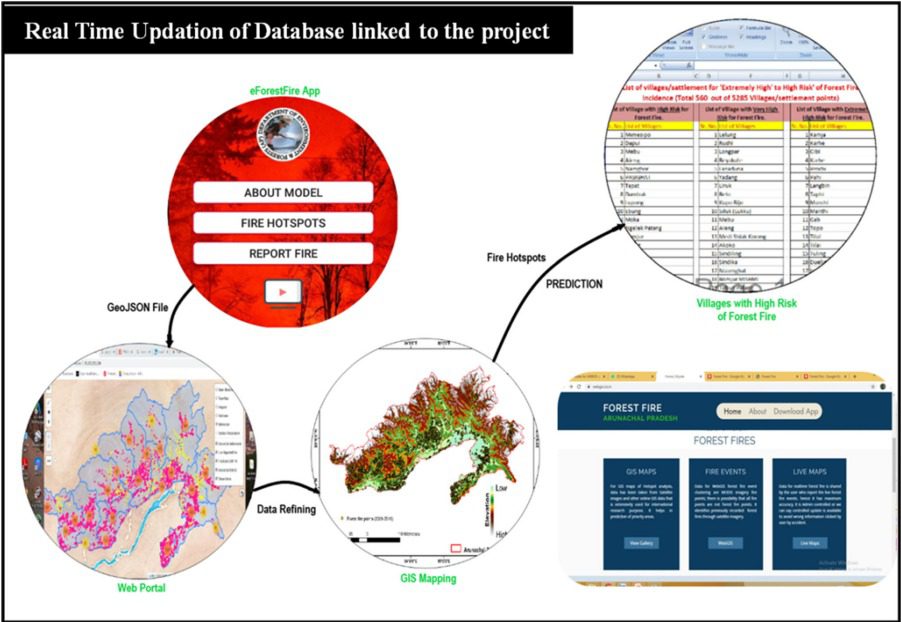
MOBILE APPLICATION
After analyzing the data and by re-studying the previous study done by the German publisher, Dr Qayum and team made a map based upon all the factors due to which forest fires were happening. Through this, two hotspots were identified, one from the FSI data and the other one from all the factors pertaining to forest fire. To verify their study, a 63 percent correlation was found, which is a high number. “Subsequently, we came up with a mobile application by the name of E-Forest Fire which was hence popularized and was sent to various divisions and district officers,” he said.
People were asked to download the app and submit the forest fire data. The correlation which stood at 63 percent earlier rose to 83 percent and the model was also more refined. The intersection of these with fire data led to identification of final hotspots within the predictive model. The model was improved by linking it to a mobile app and the WebGIS portal.
Of the 5258 settlements/villages, a total of 560 were found to be at high fire risk. Percentage correlation increased from 63 to 74, after data revision through the app. A focused intervention on predicted villages was undertaken, resulting in a decrease of 31% of fire incidence in comparison of last five years (2015–20) data. Such advanced information about fire disaster with optimal use of limited resources was greatly helpful and helped protect the rich Himalayan biodiversity.
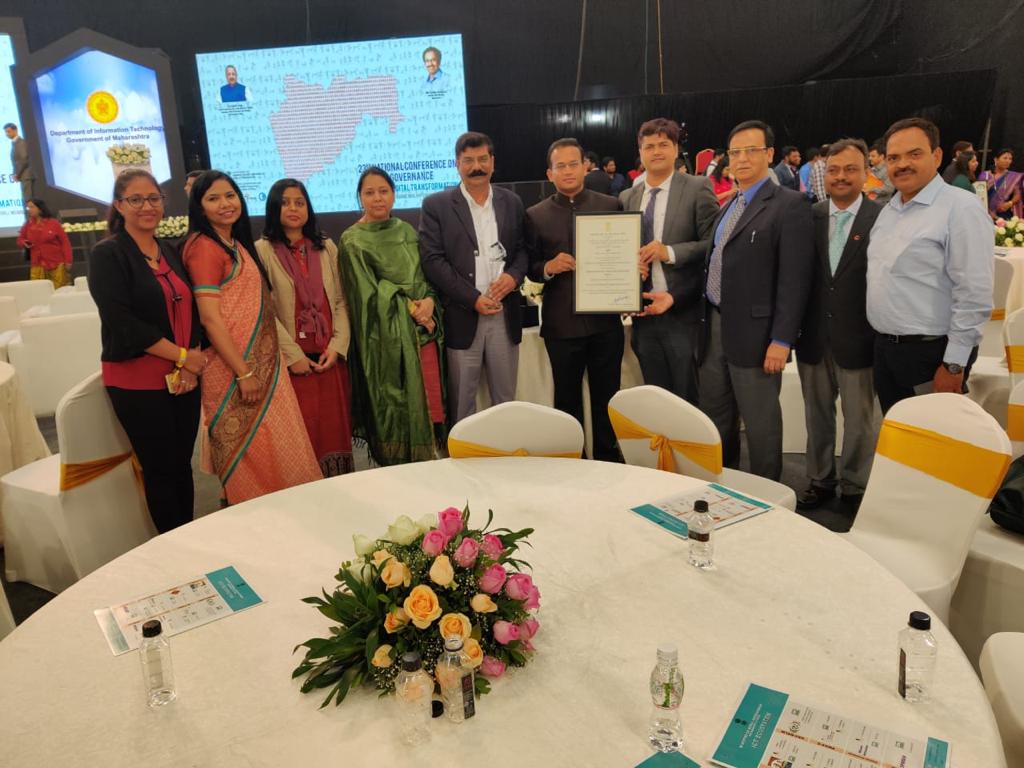
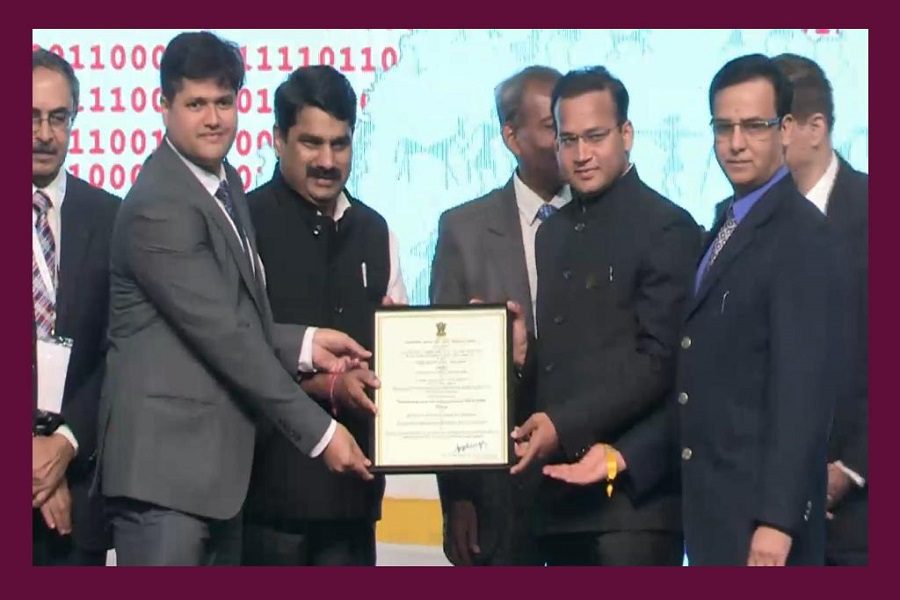
The project was recognized by the Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances, Government of India, and the officer and the whole team were presented with the National Award for E Governance 2019-2020 for eForest Fire-Himalayan Forest Fire Prediction.




































