Belur Makhana is on a rampage. The radio collared elephant killed a person in Wayanad district earlier this week. The enraged pachyderm is still moving around creating panic in North Kerala. Schools have been closed down due to its terror. As if this wasn’t enough, a tiger and a bison were also sighted in residential areas, adding to the panic.
Kerala forest department is conducting drone surveillance and using thermal camera to detect its movement. The entire forest department is on a high alert. More than 200 forest personnel accompanied by four kumki (trained and domesticated) elephants have been pressed into service to track it down. They tried to dart it with tranquiliser guns twice. But in vain.
THE INCIDENT
Belur Makhana was travelling from Karnataka’s Hasan. This elephant had earlier been radio-collared by the Karnataka Forest department and pushed back into the forest. On 10th February morning when he entered Wayanad and was moving towards the forest, the forest staff had detected its movement and had also issued alerts. Yet, the tragedy couldn’t be avoided.
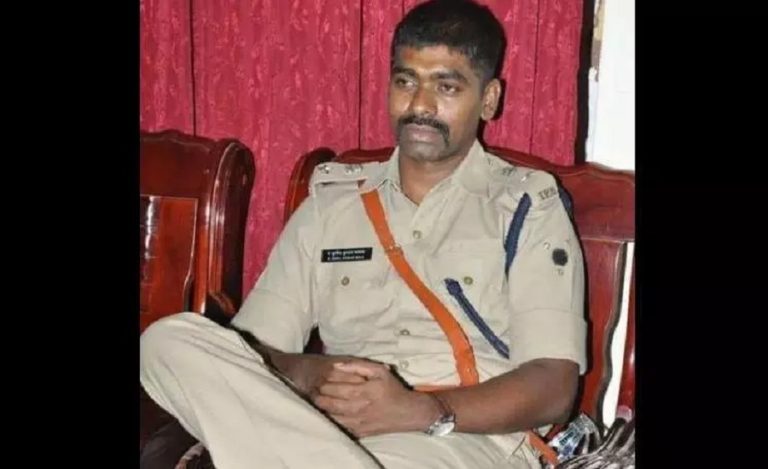
Two-three houses were present on its path. Local residents got agitated after sighting a mighty elephant moving around their houses and started chasing it. They created noise and started pelting stones at it. The elephant got irritated and identified the attackers. Most of them ran away to safety. But, one of them was seen by the elephant while trying to hide in a house and killed. “This is very unfortunate. It is the last thing we want,” Mr. D Jayaprasad told Indian Masterminds.
THE FALLOUT
Mr. Jayaprasad said that the team is trying to push it deep into the forest. “We can’t take any risk of casualty or even crop raiding now. Our team is doing the best and we are hoping for a good result very soon”.
He also emphasized that even though they have solar fencing, elephant proof trenches and task forces to deal with conflict situations, that is not enough. “We need to have more protection, as boundaries are for human, not for the wild,” he said.
THE PROBLEM
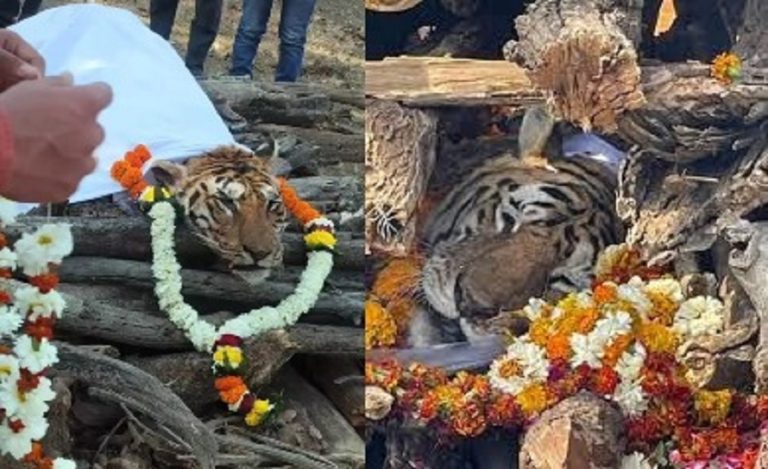
These back-to-back incidents have once again highlighted the issue of escalating human-animal conflicts in the state. Besides Wayanad, Kannur, Palakkad and Idukki are the worst-hit districts. At least 41 lives have been lost in elephant attacks and seven to tiger attacks in this region during past 10 years. The state has suffered significant crop and cattle losses as well.
Wayanad forest is part of Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve. Its boundary is contiguous with Nagarhole Tiger Reserve, Bandipur National Park, and BR Tiger Reserve in Karnataka, and Mudumalai Tiger Reserve and Sathyamangalam Forest in Tamil Nadu. While this region is significant for ecology and conservation, wild animals have been repeatedly invading human habitations while traversing the state borders in search for food.
MOOT QUESTION
The question is whether human-animal conflict can be completely avoided. The answer is a big ‘no’. “We can’t totally safeguard the area from such incidents. The forest department is doing their best but the only disadvantage is the geographical location of Wayanad,” said Mr. Jayaprasad.
The officer also highlighted that this incident could have been avoided if the communication was clear between Karnataka and Kerala Forest departments. Mr. Jayaprasad pointed out that the elephant was wearing radio collar and was tracked. Yet, when it entered Kerala, there was a delay in password sharing and providing some equipment. This delay led to the fatal accident.