Uttarakhand is on fire. Literally. The past six months have seen fires erupting, and then spreading far and wide, in over 1200 different locations. From the state Chief Minister Tirath Singh Rawat calling an emergency meeting to the Uttarakhand High Court summoning top forest officials to explain why and how the flames started spreading, concern bordering on panic is as thick as smog in the otherwise pure air of this hill station which is also known by the name of `Devbhumi’ (the land of the saints).
CHOPPERS FOR FIRE-FIGHTING
One wonders how the saints would be looking, from the ethereal heights, down on the flames which are being blamed on anything from unpredictable global warming to the human mischief. To give one example of the situation’s seriousness, the Indian Airforce recently deployed two MI17 helicopters to douse flames in the Tehri district of the strict. To the locals, it was certainly an unusual sight. The two choppers carried out several sorties, first taking water from the Tehri dam and then sprinkling it on the fire from above.
Bu this fire-fighting technique, of using choppers, may be like sending a small army of ants to stop the march of an elephant. The thought is echoed by the former Principal Chief Conservator of Forests (Uttarakhand), Mr I D Pande, when he says that this method would yield precious little. “This would be counter-productive,’’ says he, explain “by the time the helicopter flies back to get more water, the intensity of the fire would aggravate by the first action. This technique would not be effective at all.’’
Mr Pande, incidentally, is widely recognized as an authority on forest fires. He has also held the position of the director of Modern Forest Fire Control Project.
FACTORS AT PLAY
Mr Anup Sah, the well known adventurer, naturalist and a Padma Shree awardee, feels that more than one factors have contributed to the harrowing situation in Uttarakhand. It’s a well-known fact, says Mr Sah, that forest fires normally start from February onwards due to two factors: the pines and other Himalayan trees start shedding their leaves on the ground which by them had lost most of moisture in its soil. This situation leads to easy combustion and fires take place.
But this time, the fires started erupting in the Uttarakhand hills since October 2020. This happened, according to Mr Anup Sah and a number of other environmentalists, because of insufficient monsoon last year, leading to loss of moisture in the soil. The changing global weather also added its weight to the situation- resulting in a rash of out of season fires.
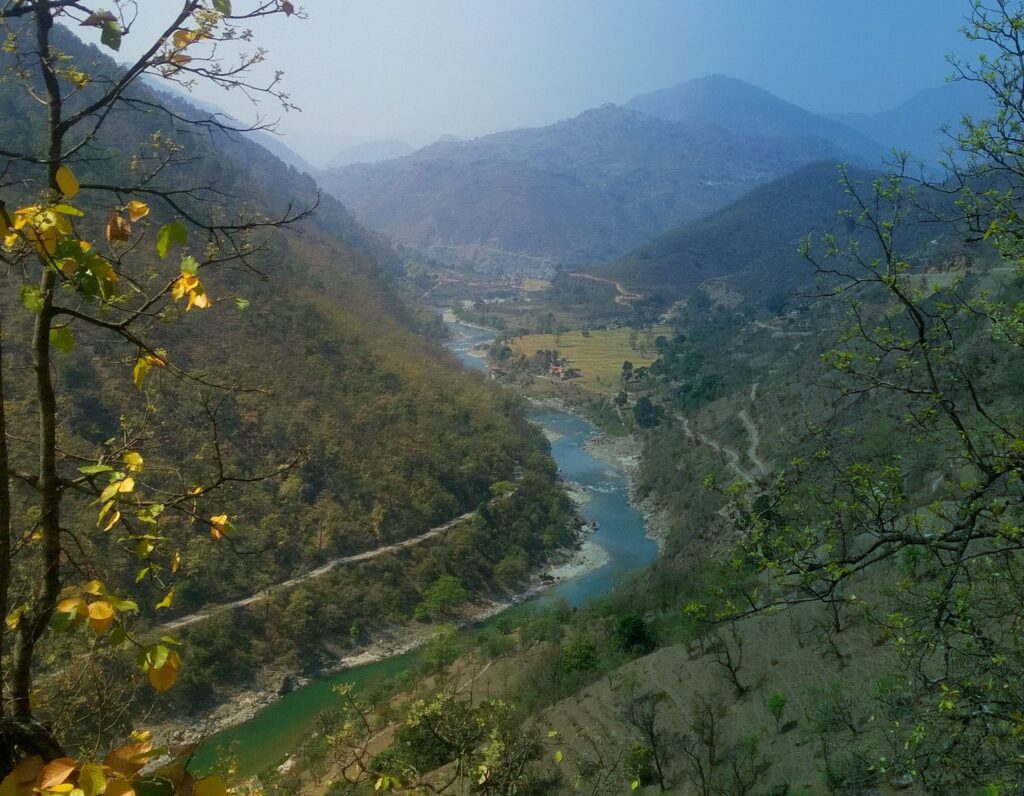

PEOPLE AT RISK
As it is, the fires have impacted most districts of Uttarakhand in more ways than one. For one, it has reduced the visibility significantly. At various places in Kumaon and Garhwal, where one could see the Himalayan peaks hundreds of kilometers away, the visibility stands reduced to mere 200 metres. The pollution is not only bodily affecting people, especially the elderly ones, but it’s having psychological fall-outs too. As the Chief Medical Officer (CMO) of the picturesque Paudi district- now under a dark shadow of smog- Dr Manoj Sharma points out, “the smoke is also causing psychological issues among the people.’’
According to the Chief Medical Officer of Pithoragarh, Dr H C Pant, “there is increase in the number of people facing irritation in eyes as well as respiratory issues.’’
The impact of forest fires has been equally brutal on the land. According to the state forest department, the fires have claimed as much as 1297.43 hectare of forest land rich in biodiversity.
And the flames are yet to be doused.