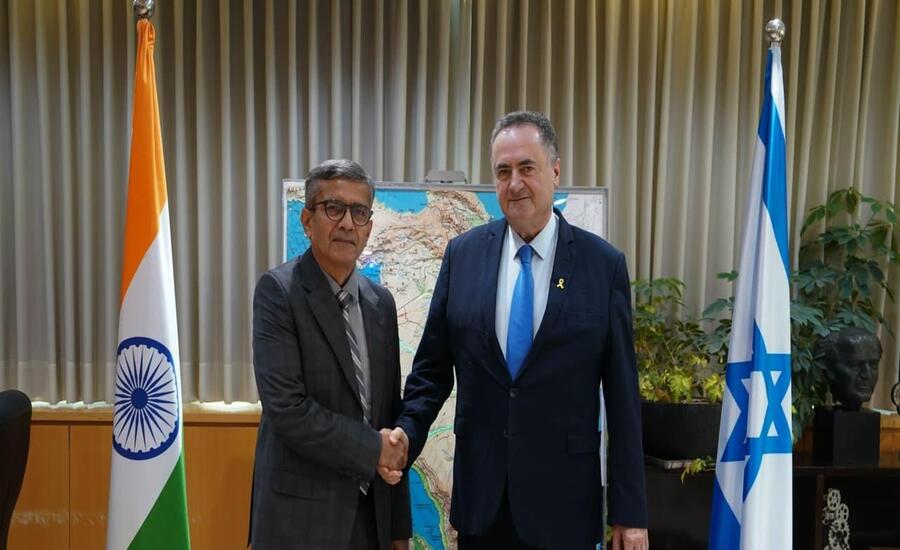
New Delhi/ Tel Aviv: In a significant step that escalates defence ties, Tel Aviv played host to the 17th meeting of the Joint Working Group (JWG) on defence cooperation between India and Israel.
During the meeting, the two nations signed a landmark Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) aimed at strengthening their strategic, technological and industrial defence partnership.
The agreement underscores shared security interests, a shifting global threat landscape and a growing emphasis on make in India manufacturing for defence.
Background of the India Israel Defence MoU
India and Israel have long maintained strong defence and security relations. Over the years, the relationship has evolved from buyer-seller arms dynamics into more sophisticated collaboration encompassing technology sharing, research & development, and joint manufacturing.
According to data, Israel has been a significant supplier of defence equipment to India, and both nations have benefited from shared intelligence, counter-terrorism cooperation and innovation in military systems.
The 17th JWG meeting builds on this legacy, reflecting both nations’ strategic impatience to adapt to emerging threats — cyber warfare, artificial intelligence (AI), unmanned systems and rapid indigenous production. With both countries emphasising self-reliance (“Make in India” for India; technology leadership for Israel), this MoU comes at a crucial time.
Major Highlights of the India Israel Defence MoU
1. Unified Vision & Policy Framework: The new MoU provides a “unified vision and policy direction” for bilateral defence cooperation. This means that India and Israel intend to move from ad-hoc projects toward systematic partnerships in defence manufacturing, innovation and training.
2. Co-Development and Co-Production: The agreement explicitly emphasises co-development and co-production of defence systems. Thus, rather than simply importing, India will increasingly work with Israeli industry to build systems on Indian soil, using shared R&D, manufacturing and technology transfer.
3. Review of Ongoing Projects & Future Roadmap: The JWG reviewed ongoing defence collaboration projects and acknowledged mutual benefits from shared expertise. The nations also discussed expanding future cooperation to match evolving threats and technological shifts.
4. Shared Security and Counter-Terror Focus: Beyond technology, the MoU reaffirms India and Israel’s joint commitment to counter-terrorism, regional stability and handling shared security challenges.
Priority Focus Areas of the India Israel Defence MoU
Key areas identified are as follows;
- Strategic dialogues and joint training initiatives.
- Defence industrial cooperation: joint manufacturing, supply-chain integration.
- Science & Technology, Research & Development.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Cybersecurity.
Strategic Implications of India Israel Defence MoU
Strengthening India’s Defence Industrial Base: For India, this pact supports the vision of self-reliance in defence manufacturing (‘Atmanirbhar Defence’) by leveraging Israeli expertise, manufacturing capability and technology. This could reduce dependency on third-party imports and bolster indigenous capability.
Technology Leap & Future-Ready Systems: With emphasis on AI, cybersecurity and advanced research, India gains access to Israeli niche technologies — drones, sensors, electronic warfare, and more. For Israel, this opens Indian markets and a partner in large-scale defence business.
Co-Production = Scale & Cost Efficiency: Co-production means shared manufacturing, which can bring down unit cost, enhance scalability and create supply chains across both countries. This is a win for defence procurement efficiency.
Regional & Global Security Impact: As India and Israel deepen cooperation, their combined capabilities send a message in regional geopolitics — reinforcing deterrence, improving readiness and increasing interoperability in joint operations. It also helps India’s role as a stabilising force in the Indo-Pacific and Israel’s outreach beyond its region.
What Lies Ahead: Key Watch-Points
- The timeline and nature of the first co-production projects, including which systems will be produced jointly.
- How the Indian defence industry and startups will integrate into this framework and benefit from technology transfer.
- Impact on procurement patterns, especially whether India reduces dependency on other suppliers.
- How the MoU addresses export potential of jointly developed systems.
- Monitoring of follow-up actions, detailed agreements, and implementation mechanisms.
Read Also: India’s Flying Thunder! 800 km Range BrahMos-ER To Become IAF’s Deadliest Weapon Yet