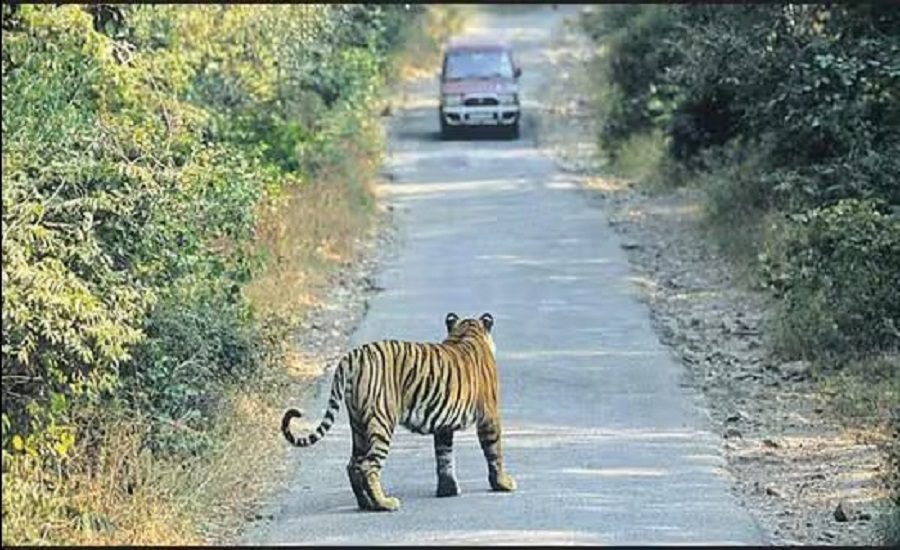
Gurugram: A tragic incident occurred early Saturday morning when a two-year-old female leopard was found dead on the Gurugram-Faridabad raising alarm over the growing issue of wildlife roadkill in the region. The leopard was discovered around 6:30 am, approximately one kilometer from the Pali police post on the Faridabad side. Preliminary investigations suggest the leopard’s death was the result of a high-speed collision, with a head injury being identified as the likely cause of death.
Divisional Forest Officer (DFO) Ramkumar Jangra said, “As per the preliminary investigation, it looks like an accident. The leopard was bleeding profusely, and the injury indicates a high-speed collision with a heavy vehicle as the probable cause. An autopsy will be conducted to confirm the exact cause.”
The postmortem, which is scheduled for Saturday, will provide further insights into the specifics of the injury and the cause of death. This unfortunate incident is not isolated, as similar roadkill cases have been reported in the area in recent years, including the death of an eight-month-old female leopard in 2015 and a 12-year-old male leopard near Manesar.
Call for Wildlife Crossings
The Gurugram-Faridabad road runs through a vital wildlife corridor that connects the Asola Sanctuary and the Aravalli Hills, both key habitats for leopards and other wildlife species. Environmentalists have long raised concerns about the risks posed by roads cutting through these natural zones, leading to frequent wildlife accidents.
Vaishali Rana, a local environmentalist, has called for the creation of wildlife crossings, such as overpasses, underpasses, or elevated road sections, to help animals safely navigate between habitats without encountering traffic. “A dedicated wildlife corridor must be created across the road. Such infrastructure would not only protect wildlife but also safeguard commuters from potential accidents,” said Rana.
These crossings are considered essential to mitigate the growing problem of wildlife roadkill, especially as urban sprawl continues to encroach upon natural habitats. If implemented, wildlife crossings would allow animals to cross roads safely and reduce the number of collisions with vehicles.
The Rising Threat to Wildlife
The road passing through the Aravalli Hills and Asola Sanctuary is a critical route for wildlife migration. However, it has increasingly become a death trap for many animals, including leopards, deer, and other species. As human settlements expand and roads intersect with natural habitats, wildlife is often forced to cross roads in search of food, mates, or territory.
The loss of these animals has serious ecological consequences, especially for species like leopards, which play an important role in maintaining the balance of the ecosystem. The disruption of wildlife corridors is leading to fragmented habitats, which could further endanger the species in these areas.
The Need for Urgent Action
The fatal collision on the Gurugram-Faridabad road highlights the growing human-wildlife conflict and the need for immediate action to protect both wildlife and human life. Wildlife experts and environmentalists are urging local authorities to prioritize the construction of wildlife crossings to address the rising number of roadkill incidents and provide a safer path for animals moving across urbanized areas.
“Without reimagining how infrastructure intersects with natural habitats, tragedies like this will continue to increase,” said Rana. She and other environmentalists are calling for swift action from authorities to protect both human and animal lives and ensure that development does not come at the cost of biodiversity.
Conclusion
The death of the leopard on the Gurugram-Faridabad road serves as a stark reminder of the urgent need to reconsider how roads and infrastructure are designed in wildlife-sensitive areas. With increasing urbanization and road expansion cutting through critical wildlife corridors, the construction of wildlife crossings has become an imperative to prevent further tragedies. As experts call for immediate policy intervention, it remains to be seen whether authorities will take swift action to safeguard both wildlife and human lives in the region.