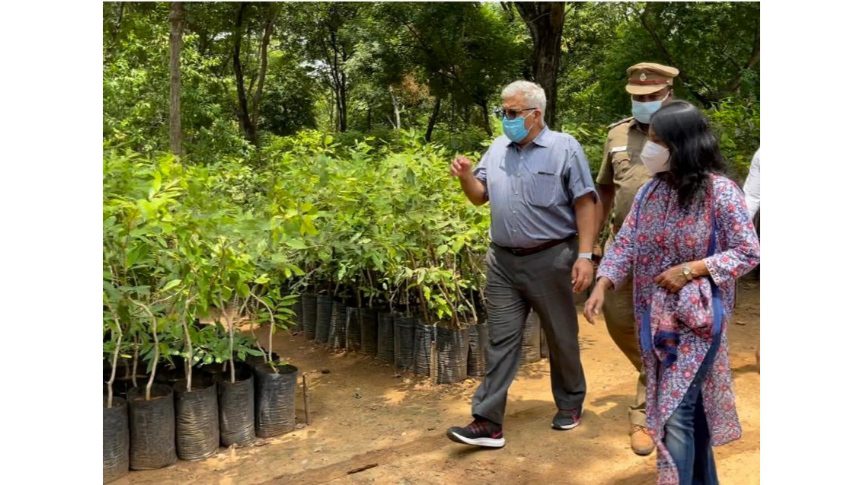
In a bid to recreate dense forests, Tamil Nadu Government has launched an ambitious plantation programme on mission mode. The programme envisaged increasing the green cover in the state for biodiversity enrichment, to mitigate the adverse impacts of climate change, soil and moisture conservation, and for augmenting the income of farming communities. In an exclusive interview to Indian Masterminds, Principal Secretary, Environment, Climate Change and Forest, Tamil Nadu, Ms Supriya Sahu, shared her vision about the Green Tamil Nadu Mission and the nurseries being readied for the project.
GREEN TAMIL NADU MISSION
“The Green Tamil Nadu Mission is about increasing the forest density in 4500 sq. kms of open forest area in 10 years period through restoration of degraded forest landscape by planting of 35-40 indigenous species,” said Ms. Sahu.
The Mission also envisages increasing the tree cover outside the forest areas by planting 260 crore seedlings in about 13500 sq kms of farmlands, fallow lands, lands of police and defence establishments, institutional lands, roadsides and panchayat tanks by the forest department, agriculture department and rural development and Panchayati Raj department in a period of 10 years.

OBJECTIVE OF THE MISSION
The Mission has some broad objectives. As per the National Forest Policy 1988 and Vision of the state government, the objective is to increase the forest and tree cover from present 23.80% of geographical area of the state to 33% by the end of the year 2030.
According to Ms. Sahu, the other objective of the mission is to augment the efforts of the Government of India in creating additional carbon sink of 2.5 to 3 billion tonne as per the commitments given under the Paris Agreement. “The State of Tamil Nadu alone proposes to create additional carbon sink of about 50 million tonne in a period of 10 years under the Green Tamil Nadu Mission,” Ms. Sahu said.

The other objective is to promote Agri Silviculture in about 8 lakh hectares of farm and fallow lands as an effective land use strategy for supplementing the income of the farming communities, as also to mitigate the adverse impacts of climate change by carbon sequestration in their lands.
Ms. Sahu also informed that to further enrich the state, they are also planting indigenous species having high air pollution tolerance index and particulate abatement capacity along the roadsides and in urban and peri-urban settings for improving the air quality index.
GEO TAGGING OF SEEDLINGS
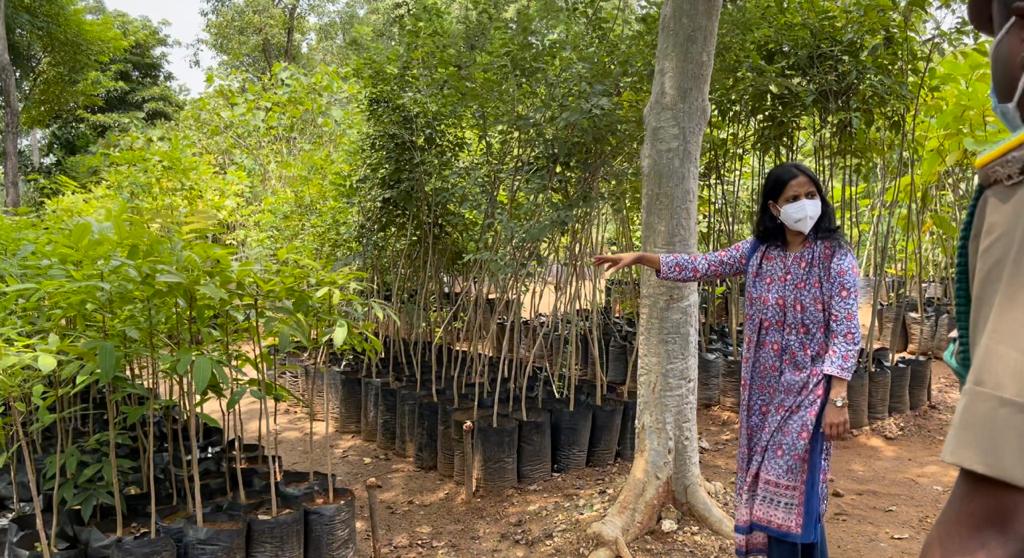
Ms. Sahu shared that in this year, they kickstarted the Mission by raising 73 lakh seedlings in 32 districts of the state. The indigenous species like Sandal, Rosewood, Terminalia spp, Emblica, Teak, Red Sanders, Pterocarpus spp, Syzygium spp, Swetenia spp, Tamarind, Pongamia, etc., was raised by the forest department and handed over to the agriculture department for planting/distribution to the farmers and general public.
We are getting nurseries ready for Green TN Mission (பசுமை தமிழகம்) which aims to increase our forest and tree cover from 23.9% to 33% #GreenTNMission #TNForest pic.twitter.com/bacRcYs88v
— Supriya Sahu IAS (@supriyasahuias) September 24, 2021
In addition, the seedlings of Casuarina (pulpwood), Melia (pulpwood and plywood), Neolamarckia cadamba (small timber and pulpwood) and Alianthus (matchwood) would be exclusively planted on farmlands for supplementing their farm income and to reduce the anthropogenic pressure on natural forests for meeting the wood demands.
“We are developing a system of geo tagging of each and every planted seedling. The planting of seedlings would be monitored 24×7 through tree clock kind of mechanism,” Ms. Sahu informed.
ECO-FRIENDLY NURSERIES

Till now the government have used polybags for raising nurseries. However, they keep the nursery and planting sites free from plastic by effective waste management strategy. “In future we plan to use biodegradable materials like coir pith to raise eco-friendly nurseries. People are free to visit the nursery site and can contact the PCCF HOD and Circle-level forest officials through Tamil Nadu Forest Department website, where address and contact details are available for public use,” Ms. Sahu said.