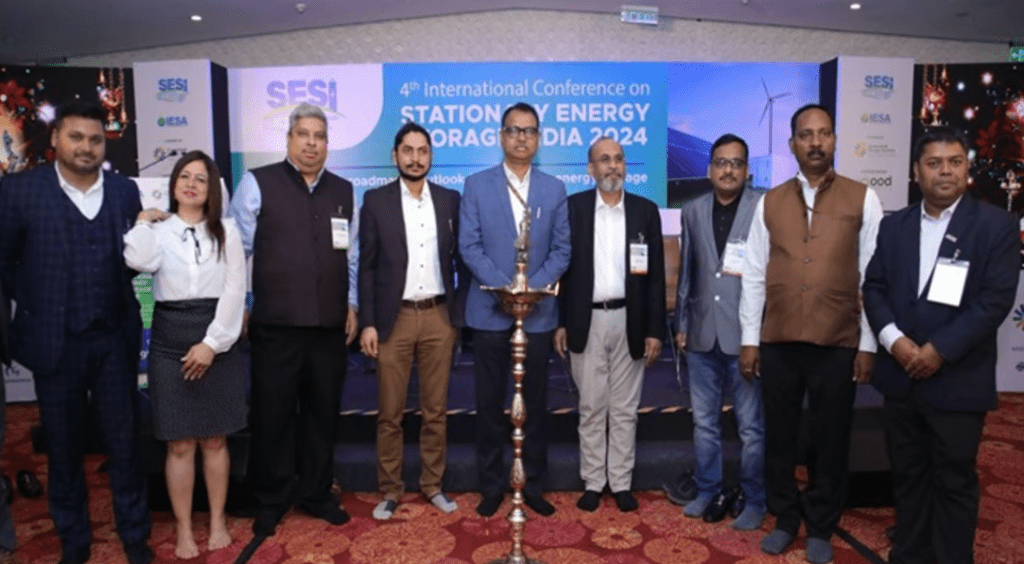
In a bid to achieve its ambitious target of 500GW of non-fossil energy capacity, India is ramping up efforts towards enhancing its renewable energy infrastructure. The 4th Edition of the International Conference on Stationary Energy Storage India (SESI) 2024 witnessed key stakeholders convening to address the imperative of integrating renewable energy into the power system.
With over 250 industry leaders, government officials, and representatives from partner countries such as the USA, Norway, Germany, Scotland, Australia, and Singapore, the conference focused on devising a strategic roadmap for bolstering renewable energy deployment, grid optimization, rooftop solar expansion, and decarbonizing the commercial and industrial sectors.
Organized by the India Energy Storage Alliance (IESA), the conference highlighted the pivotal role of advanced Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) in overcoming system integration challenges posed by the increasing penetration of renewables.
Dinesh Jagdale, Joint Secretary of the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE), underscored the importance of adopting best practices in manufacturing to support India’s evolving energy mix.
Dr. Rahul Walawalkar, President of IESA, emphasized India’s readiness for the rapid deployment of BESS and pumped hydro to complement renewable energy targets set by Prime Minister Narendra Modi. He highlighted SESI’s collaboration with various stakeholders to enact policies conducive to sectoral growth and emphasized the transition from planning to execution phase.
Rajnath Ram, Adviser (Energy) at NITI Aayog, advocated for an integrated policy framework for energy storage infrastructure to meet future energy demands effectively. He emphasized the need for scalability and flexibility in storage solutions to accommodate increasing energy generation and demand.
The Solar Energy Corporation of India Limited (SECI) recently commissioned the largest grid-connected storage project in the country, a 100-megawatt SPV solar project with a 40 megawatt/120 megawatt-hour battery energy storage system in Chhattisgarh’s Rajnandgaon district.
The conference, convened under the auspices of the Stationary Energy Storage India Council (SESI Council), witnessed active participation from key stakeholders, including regulatory bodies, policymakers, industry leaders, and international organizations. Discussions centered on advancements in stationary energy storage technologies and collaborative strategies for sectoral development.