The pine forests of Uttarakhand have long been central to resin extraction, an industry vital for manufacturing varnishes, adhesives, and turpentine oil. However, the traditional methods used for tapping resin have caused severe environmental damage. The deep cuts made into the trees not only weakened them but also contributed to forest fires and water pollution. In response to these long-standing issues, IFS officer Dharm Singh Meena has pioneered the introduction of the borehole method, an innovative, eco-friendly resin extraction technique that promises to transform the industry while safeguarding the environment.
The Problems with Traditional Resin Extraction
For decades, the Rill Method dominated the resin extraction industry in India. The technique involved making deep cuts, or “rills,” into the trunks of pine trees to induce the flow of resin. These cuts, often left open and untreated, weakened the trees, exposing them to diseases and making them more vulnerable to pests.
Moreover, traditional practices would often involve the use of corrosive chemicals such as sulfuric acid to stimulate resin flow, which would severely harm the trees over time. The resin, being highly flammable, would also drip onto the forest floor, creating tinderbox conditions in the dry season, leading to a high risk of forest fires. Additionally, during the monsoon season, rainwater would wash the resin and chemicals into nearby streams and rivers, causing significant water pollution and disrupting local ecosystems.
The Need for Innovation

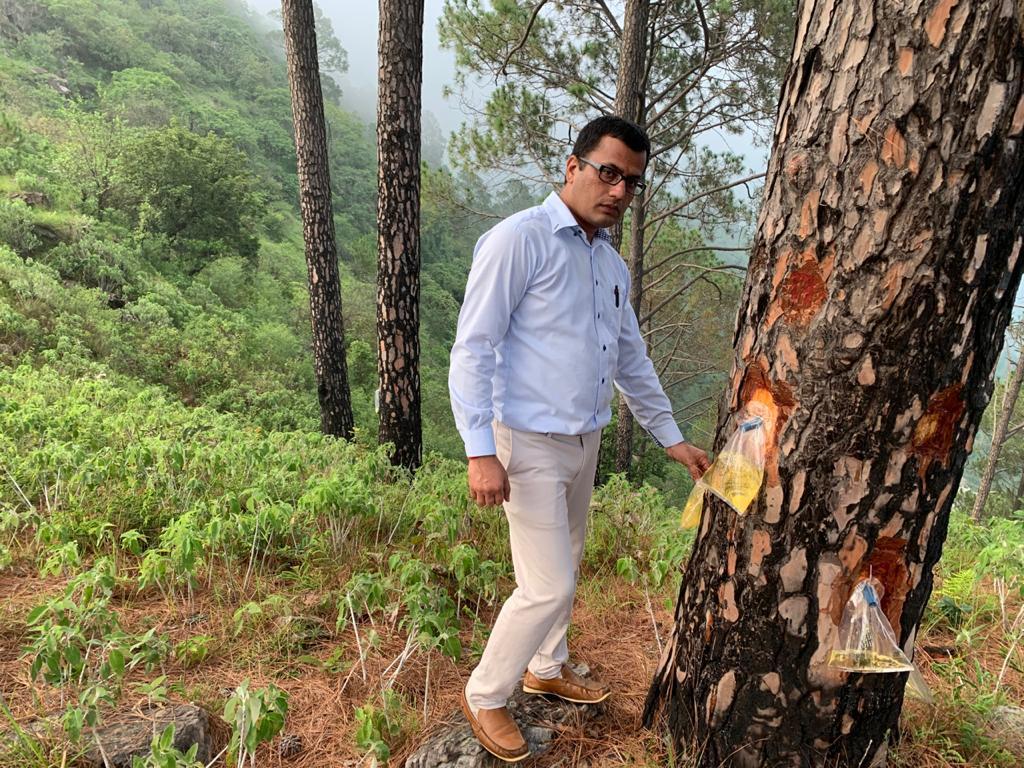
Recognizing the need for a sustainable alternative, Mr. Meena, currently posted as Conservator of Forest, Bhagirathi Circle, Uttarakhand, began working on developing a new method to minimize environmental damage while ensuring resin extraction remained economically viable. After extensive research, trials, and consultations with forestry experts, the borehole method emerged as a groundbreaking solution.
“The forests of Uttarakhand are both a resource and a treasure,” Mr. Meena told Indian Masterminds. “Our goal was to create a technology that would allow us to harvest resin without harming the trees, preventing forest fires, and protecting our water sources.”
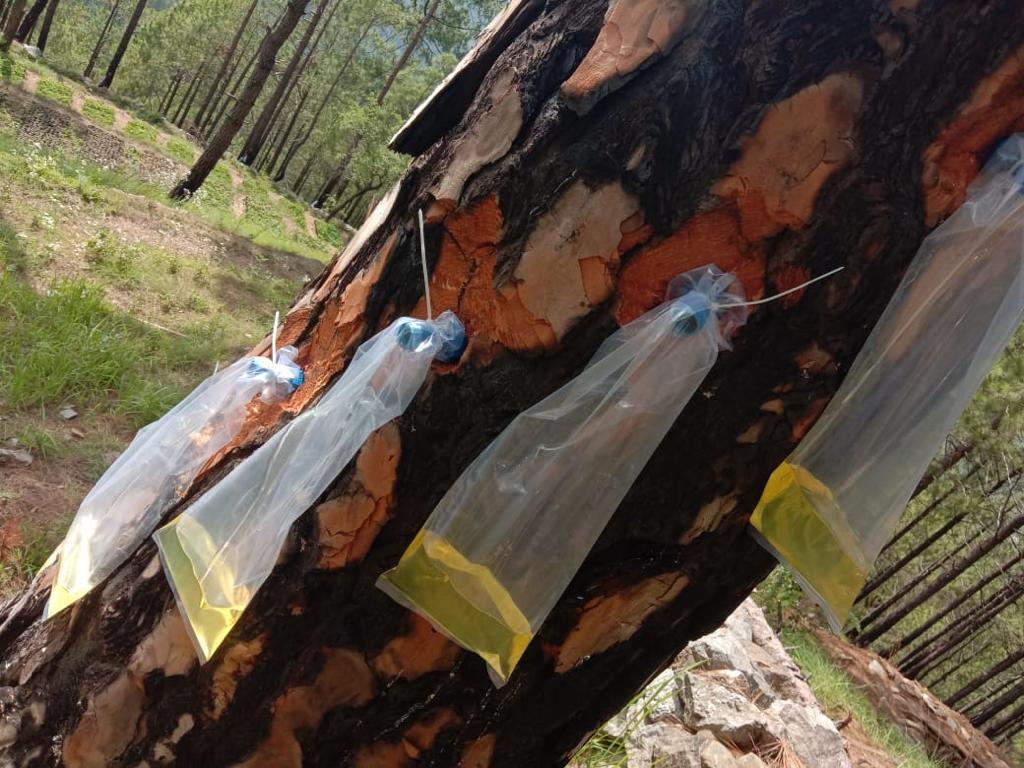
How the Borehole Method Works
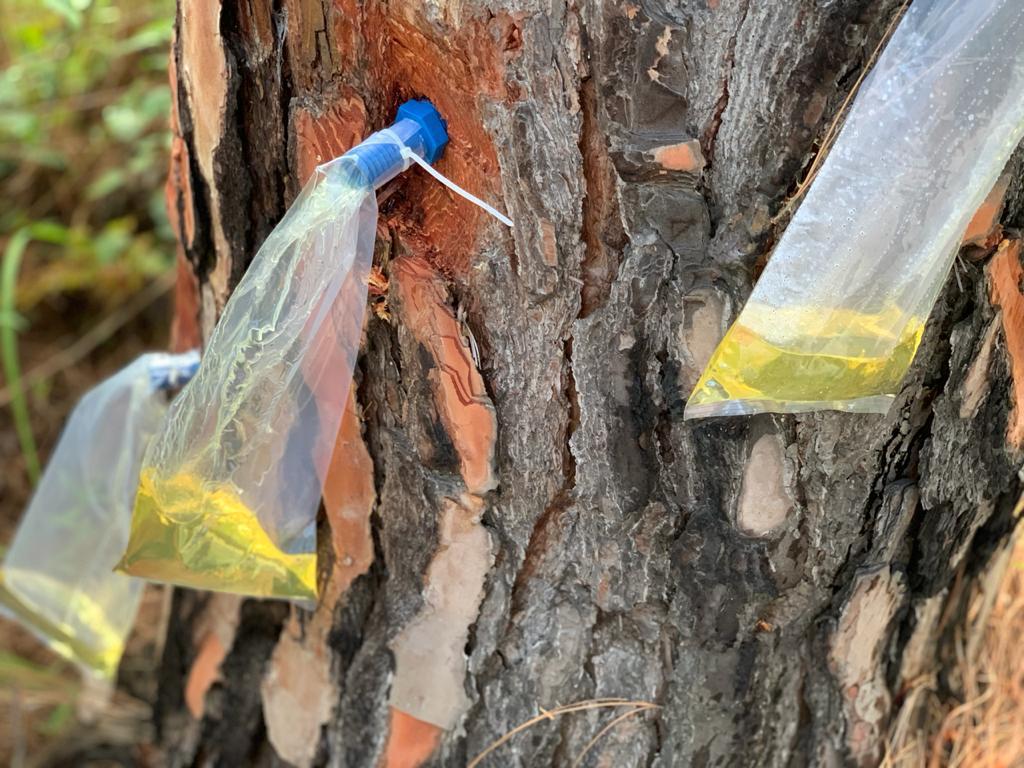
This method marks a significant departure from traditional resin extraction techniques. Instead of making large incisions into the tree bark, this method involves drilling a small, precise hole into the tree trunk. This hole, known as the borehole, is made using specialized equipment that ensures minimal damage to the tree’s vascular system.
Once the borehole is made, a collection system is installed to capture the resin as it seeps out of the hole. This collection system is sealed, preventing any resin from dripping onto the ground. The resin flows directly into a container, which eliminates the risk of environmental contamination and reduces fire hazards. Unlike the traditional method, no harmful chemicals are used to stimulate the resin flow, preserving both tree health and soil quality.

Reducing Fire Hazards
One of it’s most significant advantages is its role in reducing the risk of forest fires, which are a major concern in the pine forests of Uttarakhand. Pine trees produce resin that is highly combustible, and in the dry season, even small quantities of resin on the forest floor can become a fire hazard.
The borehole method eliminates this risk by ensuring that resin is collected directly into sealed containers, preventing any spillage onto the forest floor. This simple yet effective modification has already led to a marked reduction in fire incidents in areas where the new technique has been implemented.
“The fires we used to see every summer were devastating to both the forests and the communities living nearby,” Mr. Meena explains. “By controlling how we collect resin, we’re able to reduce the fire risk dramatically, making the forests safer for everyone.”

Preventing Water Pollution
This method also addresses a major environmental concern: water pollution. In the traditional Rill Method, resin and chemical stimulants used in the extraction process would often run off during the rainy season, polluting local water bodies. This not only harmed aquatic life but also posed a threat to drinking water supplies for nearby communities.
With this, the elimination of acids and the controlled collection of resin in sealed systems prevent these harmful substances from contaminating the soil and water sources. This is a critical improvement, particularly for regions like Uttarakhand, where many rural communities rely on streams and rivers for drinking water and irrigation.
Promoting Tree Health and Sustainable Forestry
Another key benefit is the minimal damage it causes to the trees themselves. The boreholes are small, reducing the size of the wound inflicted on the tree and allowing for faster healing. This contrasts sharply with the traditional method, where large, untreated cuts would often leave trees susceptible to disease, pests, and premature death.
As a result, trees tapped for resin remain healthier and continue to produce resin for longer periods. “The health of the trees is paramount,” Mr. Meena emphasizes. “If we want to keep benefiting from these forests, we need to ensure that our methods don’t harm the very trees we rely on.”

Economic and Environmental Benefits
The borehole method has not only provided environmental relief but also offers economic advantages. Resin collected using this technique is of higher purity, as it is uncontaminated by debris, acids, or soil. This increases the market value of the resin, benefiting local resin collectors and the broader industry.
Additionally, the new method reduces the need for re-tapping or cutting new trees, allowing for more sustainable forest management. “Our forests are living systems that must be cared for, not exploited,” Mr. Meena concludes. “With this method, we’ve found a way to balance economic needs with environmental stewardship, ensuring that these forests can thrive for generations to come.”
As this innovative technology continues to spread, it holds the potential to revolutionize how natural resources are managed, making industries like resin extraction more sustainable while preserving the delicate ecosystems of India’s forests.