New Delhi: The Union Government has outlined comprehensive steps taken to curb illegal felling of trees across the country, assuring the Parliament that the forest cover in India is on a steady rise. This information was shared by the Union Minister of State for Environment, Forest and Climate Change, Kirti Vardhan Singh, in a written reply to a question in the Lok Sabha today.
Legal Framework Governing Forest Protection
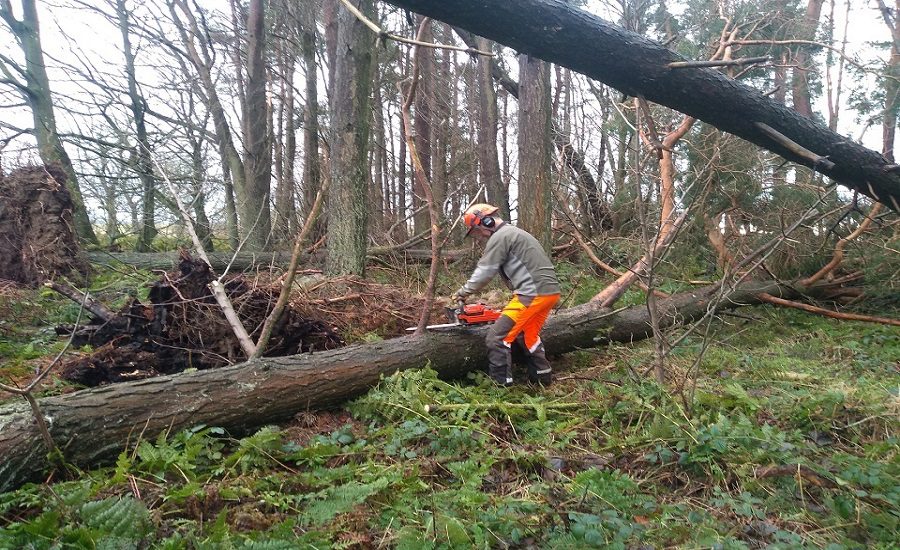
Protection and management of forests and tree cover fall primarily under the jurisdiction of the respective State Governments and Union Territory administrations. Several legislations form the backbone of forest conservation efforts in the country, including the Indian Forest Act, 1927, the Van (Sanrakshan Evam Samvardhan) Adhiniyam, 1980, the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972, as well as State-specific Forest Acts and Tree Preservation Acts. These laws ensure that any instance of illegal felling is promptly detected and offenders are prosecuted in competent courts or authorities.
Read also: Jammu’s Green Leap: Forest Department & JMC Launch First State-Owned Miyawaki Forest in Qasim Nagar
Monitoring and Data Maintenance by Local Authorities
The responsibility of assessing illegal tree felling lies with the local forest authorities, who maintain detailed records in forest offence registers. These records are maintained following guidelines prescribed by the concerned State Governments and Union Territory administrations. Such vigilant documentation facilitates targeted action against offenders and helps track the overall health of forest regions.
Positive Trends in Forest and Tree Cover
According to the India State of Forest Report (ISFR) 2023, published by the Forest Survey of India (FSI), Dehradun, India’s forest cover has increased by 156.41 square kilometers, and tree cover has risen by 1289.40 square kilometers compared to the 2021 assessment. These figures reflect the government’s sustained efforts in afforestation and forest management programs.
Key Initiatives to Prevent Illegal Felling
The government has implemented several robust measures to protect forests and prevent illegal felling, which include:
Regular Patrolling: Front-line forest staff conduct routine patrols to deter illegal activities within forest zones.
Establishment of Camps and Check Posts: Anti-poaching camps and check posts have been set up at strategic and vulnerable locations to monitor and prevent illegal logging.
Deployment of Vigilance and Flying Squads: Special teams are regularly deployed for inspections and prompt action in sensitive areas.
Community Involvement: Joint Forest Management programs engage local communities through awareness and educational campaigns, fostering collective responsibility towards forest protection.
Role of State Governments and Union Territories
While the central government provides the overarching framework and support, the execution of forest conservation strategies is primarily undertaken by State Governments and Union Territory administrations. These bodies maintain the particulars related to illegal tree felling and coordinate the enforcement of relevant laws.
Balanced Approach
The government’s response in the Lok Sabha reflects a balanced approach—acknowledging the challenges of illegal tree felling while highlighting the positive progress in forest and tree cover expansion. It underlines a commitment to strengthening forest protection mechanisms through legal enforcement, technological support, and community engagement.