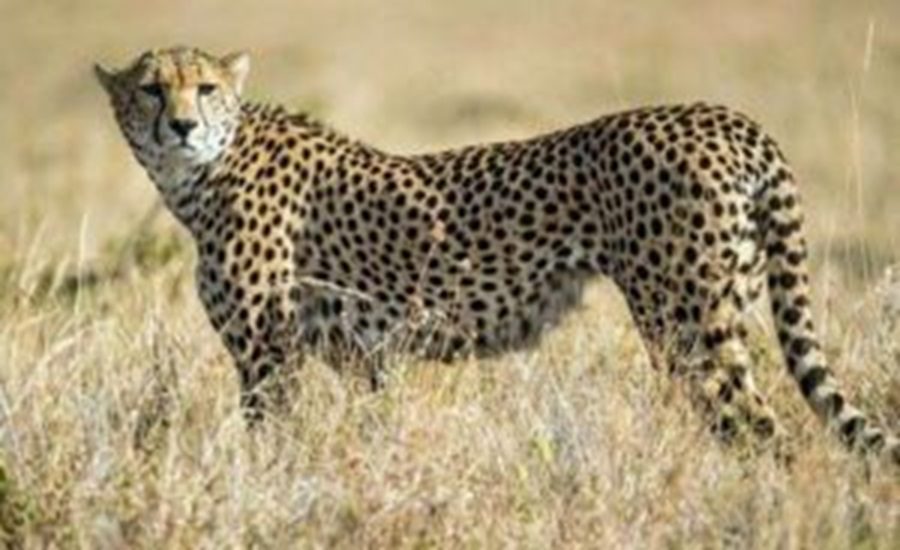
Sagar, Madhya Pradesh: In a major boost to India’s wildlife conservation efforts, the Veerangana Rani Durgavati Tiger Reserve in Sagar district is set to become the country’s first habitat where tigers, leopards, and cheetahs will coexist in the wild. The move comes as part of the long-awaited Cheetah Habitat Scheme, which is now being implemented 15 years after its conceptualization.
The decision follows a recent selection by the Wildlife Institute of India (WII), Dehradun, which shortlisted two new locations for cheetah introduction – the Banni Grassland Reserve in Gujarat and the Sagar Tiger Reserve in Madhya Pradesh.
A Unique Habitat of the Big Cat Trio
Currently, tigers and leopards roam the Sagar reserve. With the proposed addition of cheetahs, it will become the first protected area in India to host all three apex predators. Wildlife experts say this coexistence is ecologically viable, as all three cats have distinct hunting preferences and spatial behaviors:
- Tigers prey on large animals like nilgai, buffalo, and sambar.
- Leopards target medium-sized prey such as wild boar and fawns.
- Cheetahs, known for their speed, focus on small game like blackbuck and hares.
This differentiation in diet and hunting methods reduces inter-species conflict and allows for a harmonious ecosystem.
Why Sagar Was Chosen
The Muhli, Sinhapur, and Japan ranges within the reserve were surveyed by WII as early as 2010. These areas – characterized by open plains and long stretches – were found highly suitable for cheetah habitation. The total surveyed area spans approximately 600 square kilometers, while the reserve itself covers 2,339 sq km.
The site visits were conducted by NTCA DIG Dr. VB Mathur and WII Senior Scientist Dr. AA Ansari, who endorsed the landscape as apt for the project.

Challenges: Human Displacement and Budget Needs
One major challenge before cheetahs can be introduced is the relocation of human settlements, primarily Muhli village with a population of around 1,500, and others in Sinhapur and Japan ranges. The estimated budget for this displacement and rehabilitation stands at approximately ₹200 crore.
The initiative aligns with Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s conservation vision, and efforts are underway to secure the necessary funding and logistics.
Cheetahs Return After 75 Years
The project marks the return of cheetahs to India after 75 years, since they were declared extinct in 1952 due to excessive hunting. Historically, cheetahs were found from Madhya Pradesh to Punjab, but their numbers dwindled rapidly.
Now, cheetahs from Namibia, Botswana, and South Africa will be brought in under the Population Initiative of South Africa. After a quarantine and adaptation period, they will be released into the Veerangana Rani Durgavati Tiger Reserve, where tailored protection and habitat facilities are being arranged.
About Rani Durgavati Tiger Reserve
The Veerangana Rani Durgavati Tiger Reserve in Sagar, Madhya Pradesh, spans about 2,339 sq km and is named after the brave Gond queen. Rich in biodiversity, it is home to tigers, leopards, and other wildlife. With the upcoming introduction of cheetahs, it is set to become India’s first reserve where all three big cats – tiger, leopard, and cheetah – will coexist. Its open grasslands make it ideal for cheetah habitation, marking a major step in India’s wildlife conservation efforts.